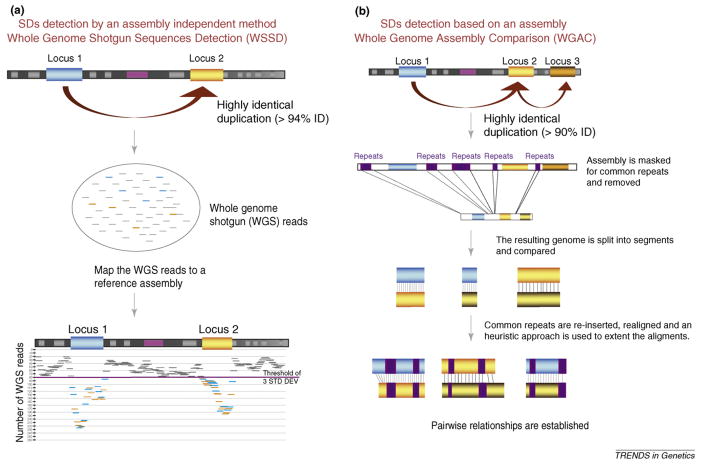
Figure I.
Strategies for duplication detection (WSSD and WGAC). (a) A schematic representation of the whole-genome shotgun sequence detection (WSSD) method to detect recent duplications. In short, whole-genome shotgun reads are mapped against a reference assembly and duplication is detected by the excess of read-depth. Thresholds for duplication detection are estimated from known single-copy BACs. (b) A whole-genome assembly comparison (WGAC) strategy where the genome is segmented, repeats are extracted and the remaining genome segments are compared to identify high identity pairwise alignments.