Figure 5.
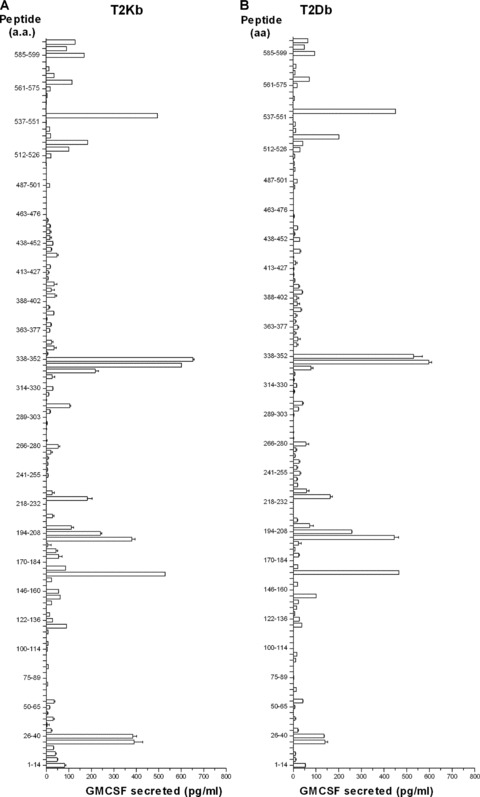
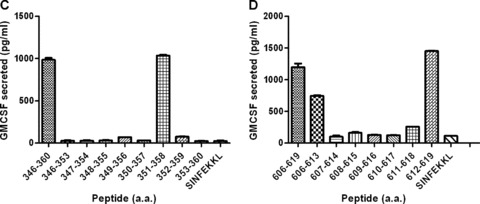
Peptide library screening of the entire mesothelin protein using immunized lymphocytes from mice receiving combinatorial T regulatory cell depletion and the vaccine identifies new mesothelin CD8+ T‐cell epitopes. (A and B) Mice received cyclophosphamide and PC61 on day 0, followed by vaccine on day 1. Spleens and lymph nodes were isolated between days 7 and 10 post vaccine, and single‐cell suspensions were stimulated in vitro in the presence of individual peptides to be tested, as described. The CD8+ T cells from these cultures were isolated in 7 days and co‐incubated overnight in the presence of peptide‐pulsed T‐2 cells expressing H‐2Kb (A) or H‐2Db (B). Culture supernatants were harvested and GM‐CSF ELISAs were performed as a means of identifying the effector CD8+ T‐cell response to the mesothelin peptides. Peptides tested were 15‐mers spanning the entire Megakaryocyte Potentiating Factor/Mesothelin precursor protein. GM‐CSF release was calculated as GM‐CSF release in the presence of T2 targets pulsed with specific peptide less GM‐CSF release in the presence of an irrelevant peptide. Splenocytes from mice immunized with the combinatorial approach were isolated 1 week after immunization and stimulated for a week with the identified 15‐mer peptides. The cells were then harvested and co‐incubated overnight with T‐2Kb pulsed with the respective 8‐mers or irrelevant controls (SINFEKKL). 8‐mers were considered for further testing when the GM‐CSF levels were higher than the ones from the 15‐mer cultures. Panel C shows the result for Meso346_360 8‐mer screening and 5D for Meso606_619 8‐mer screening. Data points shown are the mean ± SD from a representative experiment that was repeated twice with similar results.
