Figure 3.
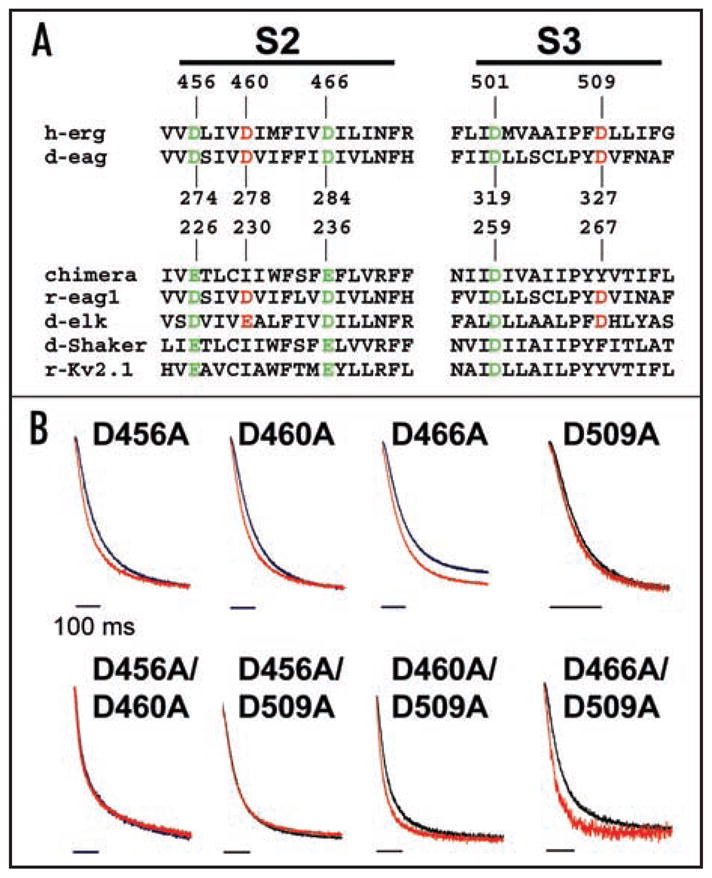
Mg2+ modulates deactivation kinetics by binding between S2 and S3. (A) Sequences of S2 and S3 segments from voltage-gated K+ channels have been aligned. Acidic residues conserved throughout the voltage-gated channel superfamily are shown in green; acidic residues conserved only in the eag subfamily of K+ channels are shown in red. Sequences from eag family members, representative members of the Kv1 and Kv2 families, and a chimeric channel in which the Kv2.1 voltage sensor paddle has been inserted into Kv1.2 are included.31,33,34,42 Members of the eag subfamily contain acidic amino acids in S2 and S3 that are not present in other voltage-gated K+ channels.30 Numbering is shown for HERG, d-eag and the chimeric channel sequences. Abbreviations used are: h, human; d, Drosophila; r, rat; erg, eag-related gene; elk, eag-like K+ channel gene. (B) Tail currents evoked upon return to −70 mV from +40 mV for single mutants or +60 mV for double mutants in the absence (black trace) or presence (red trace) of 10 mM Mg2+ have been scaled and superimposed to compare the time course of deactivation. Tail currents were fitted with single or double exponential components (thin dashed lines). Bars: 100 ms. The bath solution contained 96 mM NaCl, 2 mM KCl, 0.5 mM CaCl2, 5 mM HEPES, pH 7.5.
