Fig. 2.
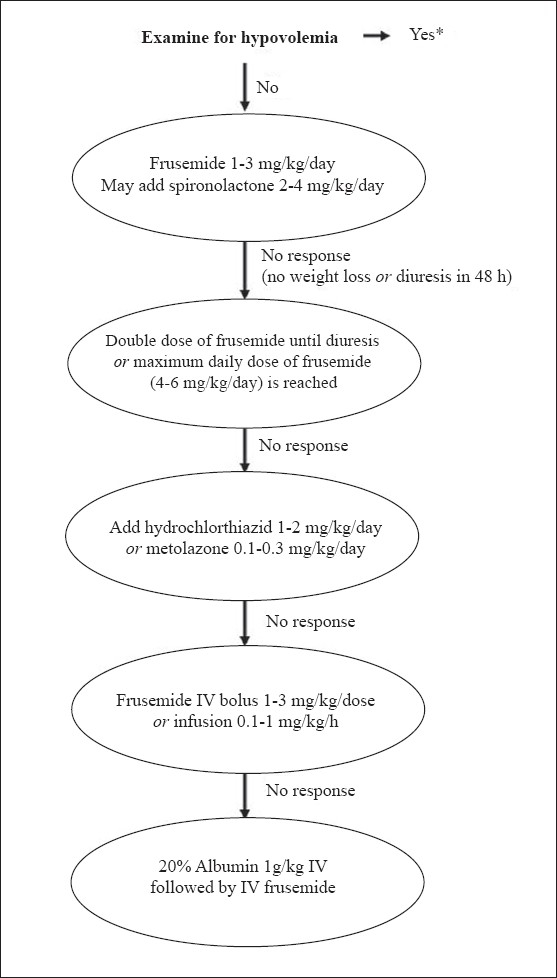
Management of edema in patients with nephrotic syndrome. Patients requiring high-dose frusemide or addition of other diuretics should be under close supervision, preferably in a hospital. Monitoring of serum electrolytes is necessary in all patients receiving diuretics. Patients showing hypokalemia require potassium supplements or coadministration of spironolactone. The medications are reduced stepwise once diuresis ensues. *Management of hypovolemia consists of rapid infusion of normal saline at a dose of 15-20 ml/kg over 20-30 min; this may be repeated if clinical features of hypovolemia persist. Infusion of 5% albumin (10-15 ml/kg) or 20% albumin (0.5-1 g/kg) may be used in subjects who do not respond despite two boluses of saline
