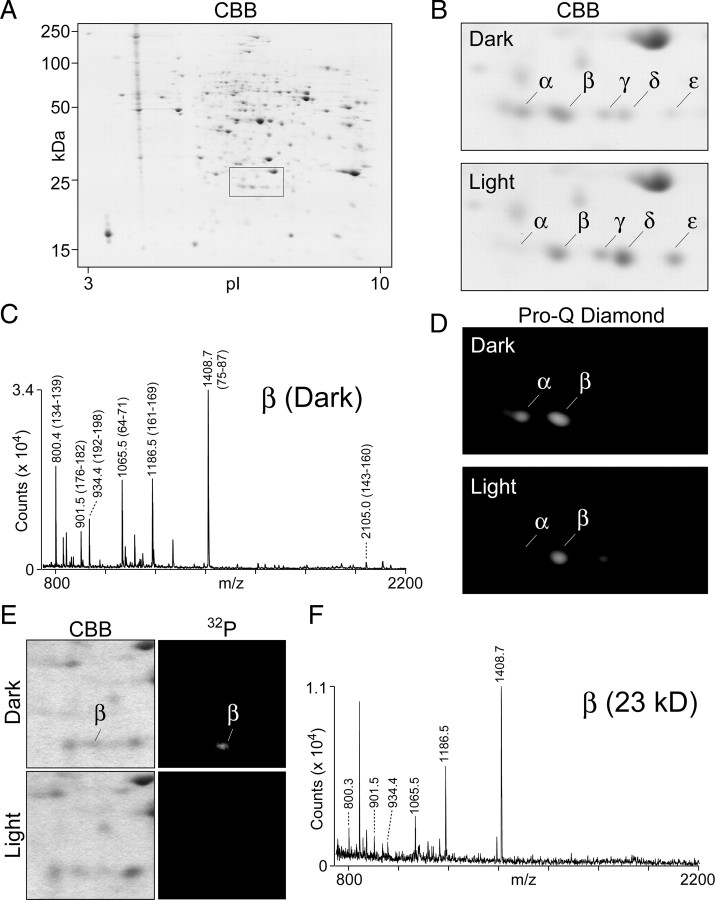
Figure 1.
Identification and characterization of RTP proteins. A, The profile of retinal proteins in dark-adapted flies as analyzed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis is shown. The boxed area identifies the location of RTP isoforms. B, The RTP region from two-dimensional profiles of retinal proteins prepared from dark- and light-adapted flies. The spots labeled α, β, γ, δ, and ε all contain the RTP protein (see Table 1). The abundance of the α spot was increased, and the δ and ε spots were decreased in the dark-adapted sample relative to the light-adapted sample. CBB, Coomassie brilliant blue. C, PMF analyses of the β spot excised from two-dimensional gel of the dark-adapted flies. The tryptic fragments labeled on the trace corresponded to peptide sequence of RTP and established that the major protein present in the β spot is RTP. The analysis was also carried on selected α, β, γ, δ, and ε spots and is summarized in Table 1. The PMF traces are shown in supplemental Figure S1 (available at www.jneurosci.org as supplemental material). D, In-gel phosphorylation analysis of the two-dimensional gel region containing RTP. The fluorescent phosphorylation sensor dye Pro-Q Diamond identified both the α and β spots in the dark-adapted profile as positive for phosphor staining. Weaker phosphor staining was seen in the light-adapted sample, and the phosphorylated α spot is greatly reduced. E, The RTP region of dark-adapted and light-adapted flies in CBB-stained two-dimensional gel (left panels) and 32P incorporation (right panels) from the analysis performed by Matsumoto and Pak (1984). The marked β spot in the dark-adapted sample showed the highest level of 32P labeling. Although the 25-year-old experiment showed more limited resolution of the spots than possible with current technology, both results show that RTP phosphorylation is reduced in the light-treated samples. F, PMF analysis of the dark-adapted β spot from the archived two-dimensional gel shown in E. The labeled tryptic fragments were derived from RTP (as identified in C), demonstrating that the major protein present in the 32P-labeled β spot was RTP.