Figure 2.
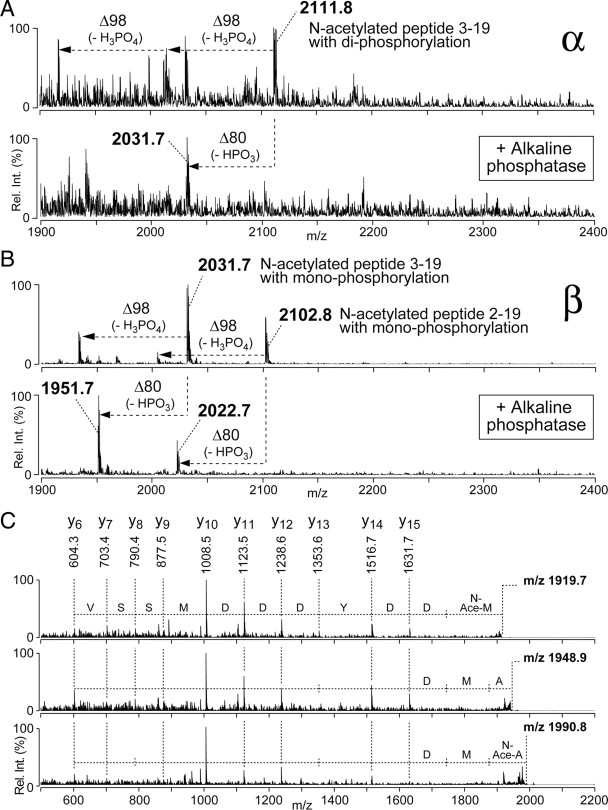
Different phosphorylation states and N-terminal modifications are found in RTP isoforms. A, Enriched phosphopeptides derived from the α spot in Figure 1B were subjected to on-target alkaline phosphatase treatment using MALDI-QIT-TOF MS. The α spot contained a peptide ion at m/z 2111.8 corresponding to peptide 3–19 of RTP (top trace). Two peaks, corresponding to single and double loss of 98 Da, characteristic of the loss of one or two neutral H3PO4, were also present. After on-target alkaline phosphatase treatment (bottom trace), a dephosphorylated peptide was generated by the loss of a phosphate group (HPO3; −80 Da). B, Enriched phosphopeptides derived from the β spot in Figure 1B were subjected to on-target alkaline phosphatase treatment using MALDI-QIT-TOF MS. The β spot contained two peptide ions at m/z 2102.8 and m/z 2031.7, corresponding to RTP peptides 2–19 and 3–19, respectively (top trace), each showing single loss of 98 Da caused by loss of H3PO4. After on-target alkaline phosphatase treatment (bottom trace), a dephosphorylated peptide was generated by the loss of a phosphate group (HPO3; −80 Da). C, MS/MS analyses on the RTP N-terminal peptide ions m/z 1919.7, 1948.9, and 1990.8. The N-terminal amino acid in the m/z 1919.8 was acetylated Met3, the N-terminal amino acid in the m/z 1948.9 was unmodified Ala2, and N-terminal amino acid in m/z 1990.8 ion was acetylated Ala2.