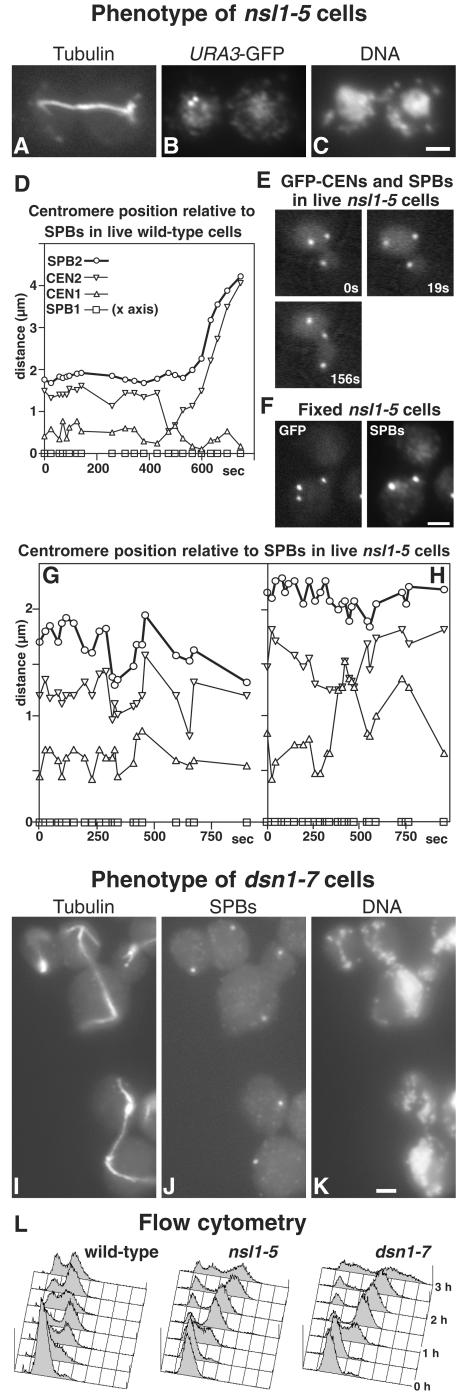
Figure 6.
Phenotypes of nsl1-5 (A–C and E–H) and dsn1-7 (I–K) mutants, and of a wild-type control (D); flow cytometry for the three strains is also shown (L). Cells were synchronized in G1 with α-factor at 23°C and released at 36°C. (A–C) An nsl1-5 cell in which the URA3 locus is labeled with GFP (strain VNY287) was fixed during anaphase (3 h after release) and processed for immunofluorescence with antitubulin (A), and anti-GFP (B), and stained with DAPI (C). Chromosome V has failed to segregate. (D–H) Imaging of GFP-labeled SPBs and CEN5 in wild-type (D, strain K8572) and nsl1-5 cells (E–H, strain VNY122). (D) A wild-type cell underwent centromere pairing and passed through anaphase during the period of observation. (E) An nsl1-5 cell where the centromeres failed to split. (F) A fixed nsl1-5 cell was processed for immunofluorescence using anti-GFP and anti-Tub4p to identify SPBs. Centromeres (the lowest GFP spot) have not split. (G) One of the majority of nsl1-5 cells, in which the centromeres split but failed to pair during the period of observation. (H) An nsl1-5 cell in which pairing occurred. Symbols in G and H are the same as in D. (I–K) dsn1-7 cells (strain VNY96) were processed for immunofluorescence 2.5 h after release using antitubulin (I), anti-Tub4p for SPBs (J), and DAPI (K). Two anaphase cells that have failed to segregate DNA and one aploid cell (top left) are shown. (L) Flow cytometry of wild-type (K699), nsl1-5 (VNY72), and dsn1-7 (VNY96) cells. Bars, 2 μm.