Figure 2.
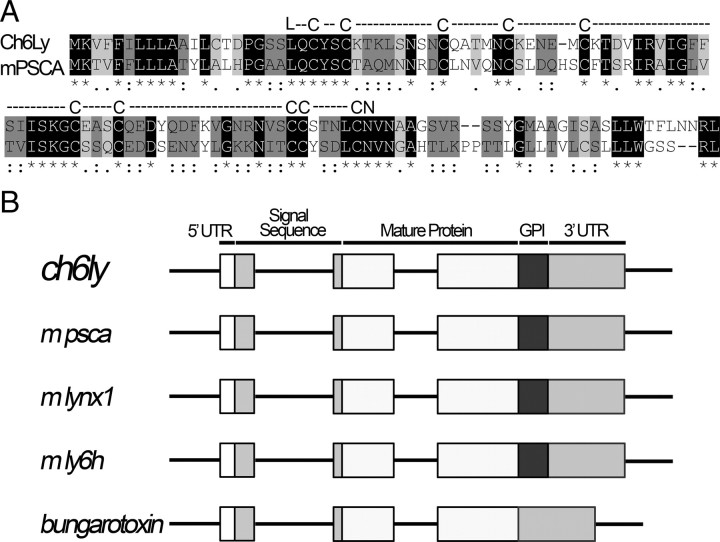
Ch6Ly is psca. A, The amino acid sequence of ch6Ly was used to search NCBI and Ensembl databases and found to have the most significant match to mouse psca. The two sequences share 80% homology and 40% identity. Black highlight indicates positions with single, fully conserved residues. Dark gray highlight indicates that the strong amino acid groups are fully conserved. Light gray highlight represents the fully conserved weak amino acid groups. Both molecules contain the cysteine-rich Ly6 domain (shown above the amino acid sequence) with conserved N-terminal leucine and C-terminal asparagine. B, Representation of the open reading frame of the genes encoding ch6Ly and mouse psca compared with the other members of Ly6/Neurotoxin superfamily such as lynx1, ly6 h, α-bungarotoxin. The ch6ly and psca have the same intron/exon breaks as the other members of the superfamily. The 5′ UTR sequence, signal sequence, mature protein containing Ly6 domain, hydrophobic GPI anchor and 3′UTR sequence are also conserved between ch6ly, psca and other members of the family.