Fig. 5.
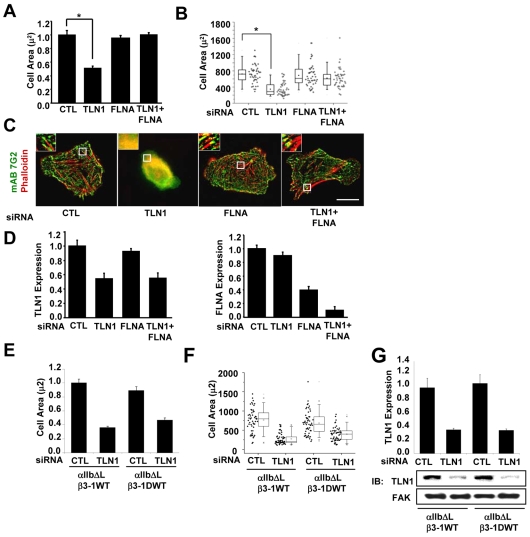
FLNa inhibits outside-in signaling-dependent events when talin-1-depleted cells are adhered by constitutively activated WT integrins. CHO K1 cells were transiently transfected with control siRNA, TLN1 siRNA#1 or FLNA siRNA#1, or both TLN1 and FLNA siRNA for 48 hours (for details see Materials and Methods), and then co-transfected for 24 hours with expression vectors for αllb-ΔL along with the β3-1A WT or β3-1D WT integrin subunits. Aliquots of transfected cells were used to confirm knockdown and to assay cell spreading and stress fibers following adhesion to fibrinogen for 1 hour in CCM1. (A) Plotted is the average cell area ± s.d. from three independent experiments (n=150). (B) Areas of individual cells from one of these experiments are depicted in a box and whisker plot (*P<0.05). (C) Localization of the recombinant integrins visualized by staining with monoclonal antibody 7G2 against human β3 subunit (green) together with phalloidin for actin filaments (red). (D) The efficiency of talin-1 (left) and FLNa (right) knockdown was determined by western blotting. Plotted is the average expression level of the indicated proteins ± s.d. from three independent experiments shown in A-C. (E) Plotted is the average cell area ± s.d. of cells expressing αIIb-ΔL/β3-1A WT or αIIb-ΔL/β3-1D WT (n=150). (F) Areas of individual cells from one of these experiments are depicted in a box and whiskers plot (*P<0.05). (G) The efficiency of talin-1 knockdown was determined by western blotting. Plotted is the average expression level of the indicated proteins.