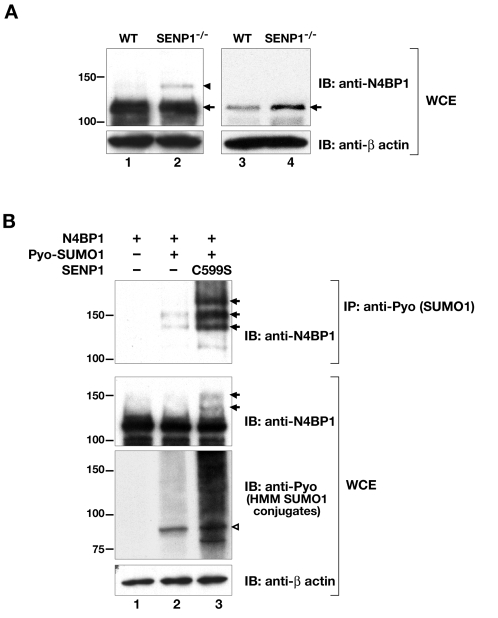
Fig. 4.
N4BP1 is SUMO1 conjugated and desumoylated by SENP1. (A) Immunoblot (IB) analysis of whole-cell extracts (WCE) of wild-type (WT, lanes 1 and 3) and SENP1-mutant (SENP1−/−, lanes 2 and 4) MEFs with anti-N4BP1 to detect endogenous N4BP1. Filters were reblotted with anti-β-actin to ensure equal loading. Arrow indicates position of endogenous N4BP1. Arrowhead indicates position of a higher molecular mass species (obvious in lane 2), presumed to be sumoylated N4BP1, seen in long exposures of immunoblots with at least 100 μg total protein (lanes 1 and 2). Immunoblotting of less total protein (10-20 μg) revealed significantly greater N4BP1 levels in SENP1-mutant cells (lanes 3 and 4). (B) N4BP1 was overexpressed in HEK293 cells with or without Pyo-SUMO1, and with or without SENP1 C599S active-site mutant. Immunoprecipitation (IP) was performed with anti-Pyo to pull down Pyo–SUMO1-conjugated proteins, followed by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-N4BP1 to detect sumoylated N4BP1 isoforms (upper panel). The arrows indicate three N4BP1 isoforms with sizes consistent with conjugation of one, two and three Pyo-SUMO1 moieties, the levels of which were enhanced in the presence of the SENP1 active-site mutant (lane 3). The middle panel shows immunoblotting of whole-cell extracts (WCE) with anti-N4BP1, revealing sumoylated N4BP1 in the presence of SENP1 C599S (lane 3, arrows). The lower panel shows immunoblotting of whole-cell extracts with anti-Pyo to detect high molecular mass (HMM) Pyo-SUMO1 conjugates. The open arrowhead points to the position of SUMO1-conjugated RanGAP1.