Fig. 1.
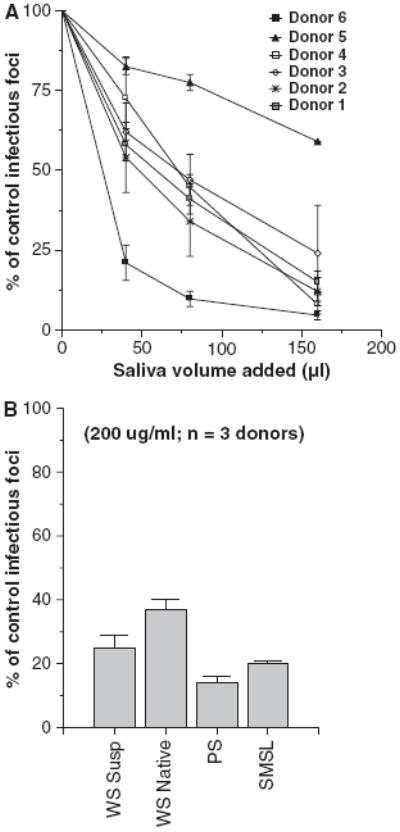
Saliva of healthy volunteers inhibits infectivity of influenza A virus (IAV). Whole saliva obtained from a panel of healthy volunteer donors was tested for the ability to neutralize the Phil82 strain of IAV using the infectious focus assay (A). Each saliva preparation caused significant dose-related reduction in viral infectivity. Results are expressed as mean % of control infectivity (n = 3 or more for each saliva sample). The neutralizing activity of whole saliva (supernatant or native), or parotid or SMSL secretions from three donors was compared (B). Neutralizing activity was present in all of these preparations (all P < 0.05 compared to control). Results were normalized to 200 μg/ml saliva protein.
