Fig. 6.
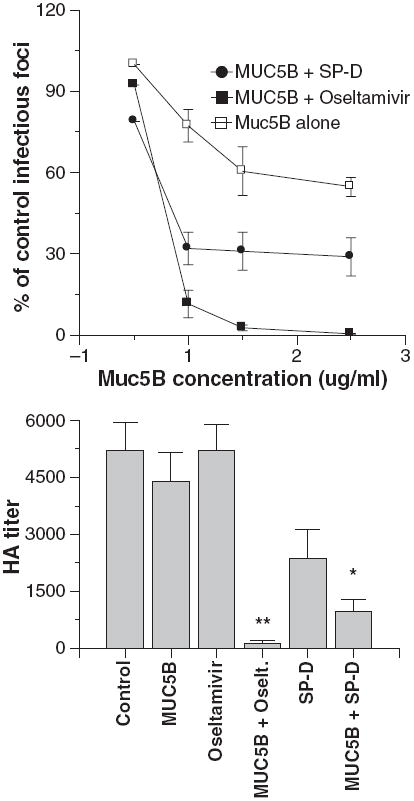
Oseltamivir and surfactant protein D (SP-D) potentiate viral neutralization and hemagglutination (HA) inhibition caused by MUC5B. In the left panel viral neutralization was measured as in Fig. 3. The Phil82 strain of virus was preincubated with the indicated concentrations of MUC5B alone or with MUC5B combined with either 250 ng/ml oseltamivir or 6 ng/ml human SP-D dodecamers. Inhibition caused by the combinations of either SP-D or oseltamivir with MUC5B caused significantly greater neutralization than either treatment alone (n = 5; significance assessed by analysis of variance). HA titers were measured on viral samples used in the aggregation assays shown in Fig. 5 and are shown in the right panel. The combination of oseltamivir and mucin caused markedly greater inhibition than either agent alone (n = 4; significant by analysis of variance as indicated by **). The combination of SP-D and MUC5B caused significantly greater inhibition than MUC5B alone but not than SP-D alone (indicated by *).
