Figure.
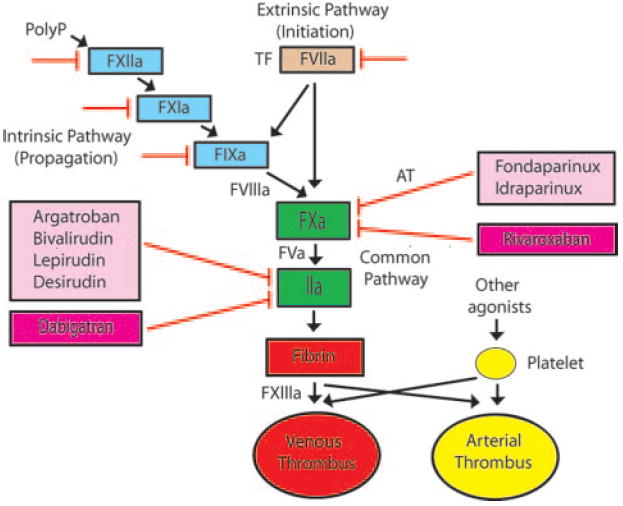
Targets of new anticoagulant drugs. The tissue factor (TF)–factor VIIa complex initiates clotting, the intrinsic pathway mediates propagation, and the common pathway results in the generation of large amounts of thrombin (factor IIa), which is the central protease in the coagulation cascade. Venous (red) and arterial (yellow) thrombi contain different proportions of fibrin and platelets. Parental direct thrombin inhibitors and factor Xa inhibitors are shown in the light pink boxes. Fondaparinux and idraparinux require antithrombin (AT) for inhibition of factor Xa. Oral inhibitors of thrombin and factor Xa are shown in the dark pink boxes. Other possible targets of anticoagulant drugs include factor VIIa, factor IXa, factor XIa, and factor XIIa (red lines).
