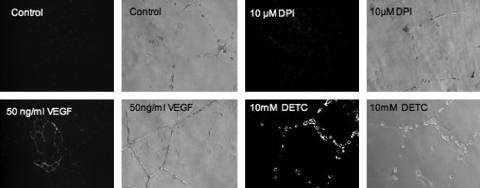
FIG. 2.
An example of the impact that ROS make on in vitro endothelial tube formation in response to VEGF treatment. Either decreasing or increasing ROS [dark images, with the amount of white color (DHE fluorescence) proportional to ROS] with DPI (flavin-containing oxidase inhibitor) or DETC (SOD1 and SOD3 inhibitor), respectively, blunts VEGF-induced tube formation on Matrigel. VEGF increased ROS production from controls (untreated cells). These observations are consistent with the redox-window hypothesis for growth-factor signaling, in that a shift toward either a reductive or oxidative state will corrupt redox-dependent growth-factor signaling. [Adapted from Rocic et al. (85), with permission.]