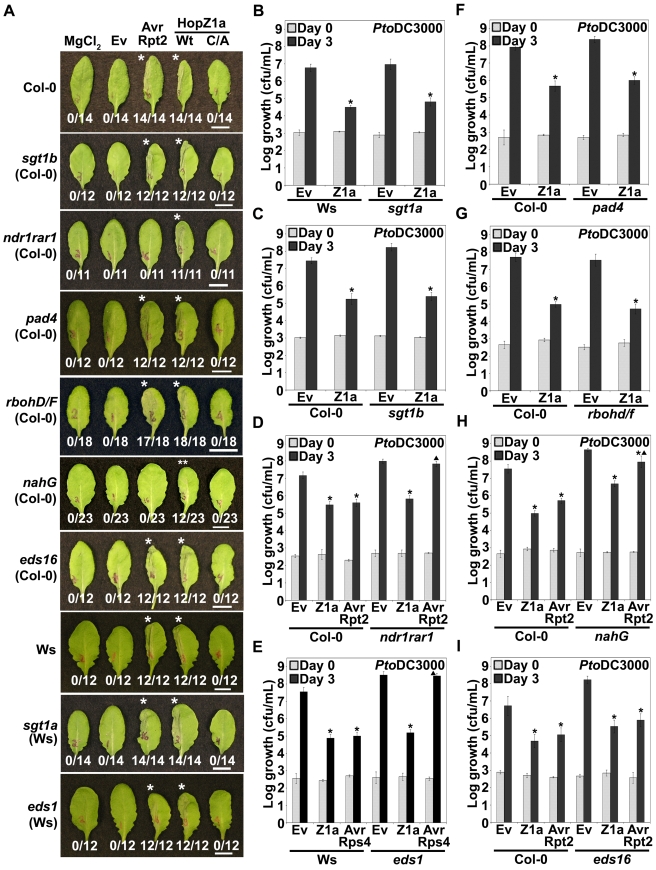
Figure 1. HopZ1a recognition is independent of known signaling components of R gene- mediated immunity.
(A) Half-leaves of Arabidopsis Col-0, Ws-0 or mutant plants were infiltrated with 10 mM MgCl2 or with PtoDC3000 expressing the empty vector (Ev), AvrRpt2, or HopZ1a or HopZ1aC216A (C/A) with a C-terminal HA tag under its endogenous promoter. C216 of HopZ1a is part of the predicted catalytic triad and the mutant protein is expressed at a similar level to HopZ1a [39]. The bacteria were syringe infiltrated into the leaves at 5×107 cfu/mL. Photos were taken 22 hours post-infiltration. The number of leaves showing an HR is indicated below the appropriate construct. HRs are marked with an asterisk. Patchy HRs are marked with a double asterisk. Scale bar is 1 cm. (B–I) PtoDC3000 expressing the indicated construct was syringe infiltrated at 1×105 cfu/mL into Arabidopsis Col-0 or mutant leaves and bacterial counts were determined one hour post-infection (Day 0) and 3 days post-infection (Day 3). Two-tailed homoschedastic t-tests were performed to test for significant differences. Within a plant genotype, treatments were compared to empty vector and significant differences are indicated by an asterisk (* P<0.01). To compare between plant genotypes, growth of PtoDC3000 carrying HopZ1a, AvrRpt2 or AvrRps4 was normalized to the average growth of PtoDC3000(Ev). Significant differences in growth of a P. syringae strain between a mutant genotype and wild type Col-0 or Ws are indicated by a triangle (▴ P<0.01). Error bars indicate the standard deviation from the mean of 10 samples. Growth assays were performed at least 3 times. Arabidopsis genotypes are: (B) sgt1a (C) sgt1b (D) ndr1rar1 (E) eds1 (F) pad4 (G) rbohd/f (H) nahG (I) eds16.