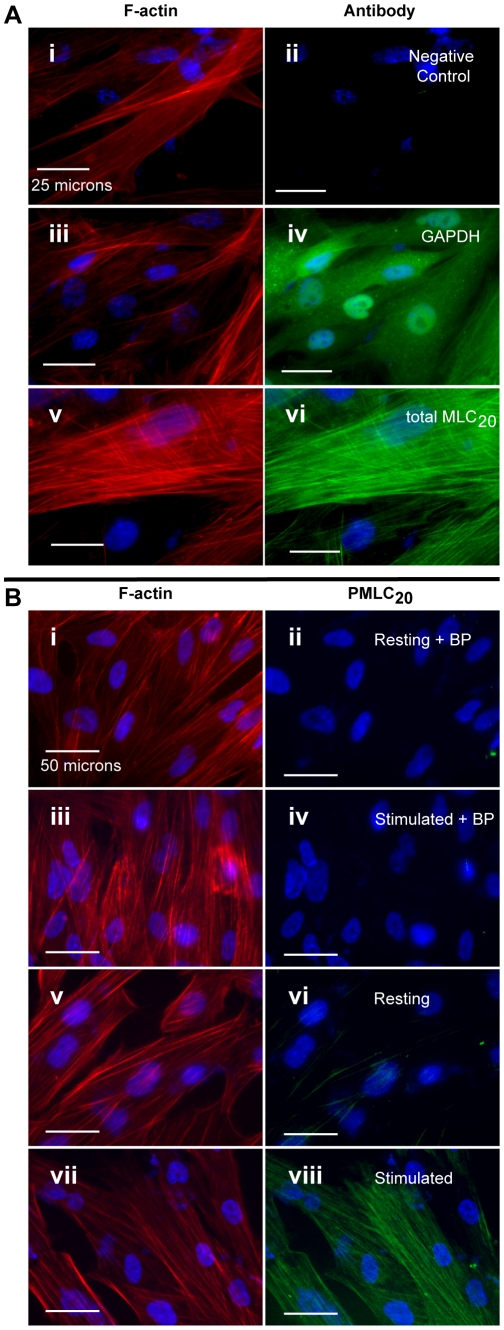
Figure 4. Antibody specificity using the in-cell western assay.
In each pair of micrographs, the left panel illustrates filamentous actin (F-actin) stained with rhodamine-phalloidin (red). The corresponding right panels are immunofluorescence micrographs stained with antibodies conjugated to Alexa-Fluor 488 (green). Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue) in all panels. Images are shown at 400× and 200× magnification in panels A and B, respectively. White bars represent 25 and 50 microns, respectively. A. Demonstration of GAPDH and total MLC20. Panels i and ii. The actin fibers stain in a filamentous pattern typical of uterine smooth muscle. There is no detectable signal with omission of the primary antibodies. Panels iii and iv. The GAPDH staining shows a diffuse cytosolic pattern in contrast to the fibrillar pattern of actin. Panels v and vi. Total MLC has a similar staining pattern to actin. B. Demonstration of PMLC20. Panels i–iv. There is no detectable background fluorescence when the antibody has been preadsorbed with blocking peptide (BP) containing phospho-Ser19 of MLC20, either in the resting state (panel ii) or with stimulation using 100 nM OT (20 sec stimulus, panel iv). Only a small amount of PMLC20 is detectable in the resting myocyte (panel vi) but this is markedly increased upon stimulation with OT (100 nM, 20 sec: panel viii).