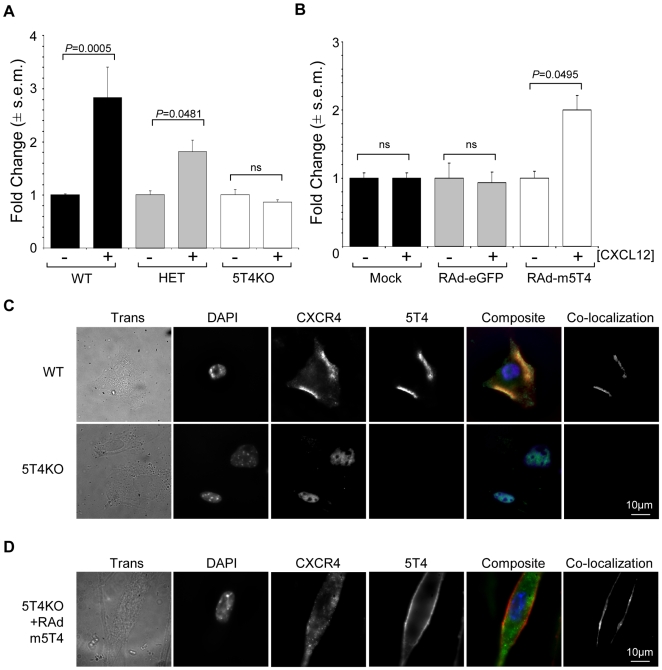
Figure 4. Role of 5T4 expression in the CXC12/CXCR4 axis in MEF.
(A), MEF derived from wild-type, (WT, black columns), 5T4 heterozygote, (HET, grey columns) and 5T4 null, (5T4KO, white columns) embryos show 5T4 gene dose related CXCLl2 chemotaxis. (B), Chemotaxis of 5T4KO MEF following mock infection, (black columns), or infection with RAd-eGFP, (grey columns), or RAd-m5T4, (white columns); CXCL12 chemotaxis is only restored by RAd-m5T4. (+ or – 30 ng CXCL12). (C), Pattern of expression of CXCR4, (green) and 5T4, (red) in WT and 5T4KO MEF. In WT cells, CXCR4 and 5T4 are seen at the cell surface and clearly co-localize (CXCR4 = green; 5T4 = red; composite: co-localization = yellow; co-localized areas shown in separate channel) while in 5T4KO cells CXCR4 is located intracellularly around the nucleus; compare to DAPI labeling (blue). (D), 5T4KO MEF infected with RAd-m5T4 exhibit cell surface expression of both 5T4 and CXCR4 also displayed by co-localization (5T4 = red; CXCR4 = green; composite co localization = yellow; co-localized areas shown in separate channel). RAd-GFP had no effect on CXCR4 expression (not shown).