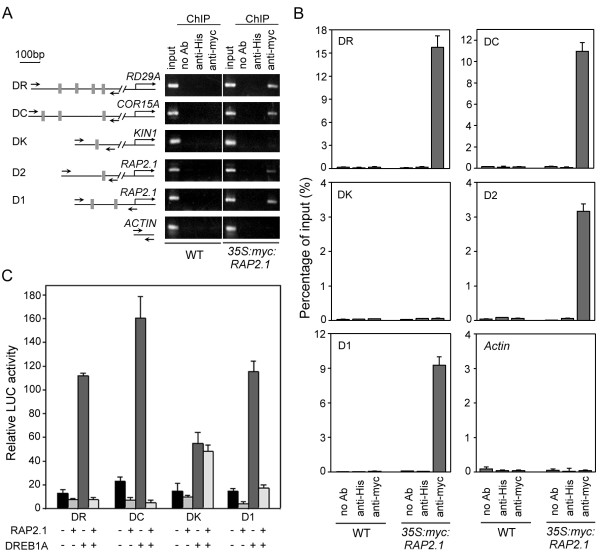
Figure 4.
RAP2.1 binds in vivo to the promoters of both RD/COR genes and RAP2.1 itself, and acts as a transcriptional repressor. (A) Semi-quantitative PCR from ChIP of samples showed specificity of DNA binding for RAP2.1. Scheme of the gene promoters studied is shown, with gray boxes indicating potential DRE/CRT sites and their positions relative to the putative ATG sites (left panel). The positions of PCR primers used to amplify each fragment were also indicated (small black arrows). Two-week-old seedlings of wild type (WT) and 35S:myc:RAP2.1 (line 5) were treated with cold for 12 h and then analyzed with or without (no Ab) antibodies specific for the myc-epitope (anti-myc) or the His-tag (anti-His). The ACTIN fragment was used as a negative control. (B) ChIP analysis of RAP2.1 binding to promoters in extracts prepared as described in (A) using real-time PCR. (C) Repression of immunoprecipitated fragment-driven reporter gene activity by RAP2.1. Values shown are means of data from three independent experiments; error bars indicate SD.