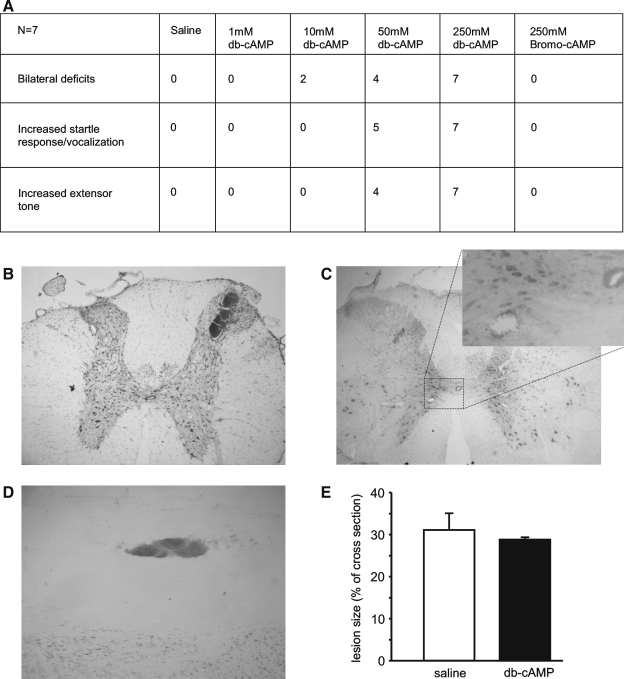
FIG. 3.
Effects of intrathecal cAMP analog application in spinal cord injured rats. Following unilateral cervical lesions, dibutyryl-cAMP (db-cAMP) application at concentrations in excess of 1 mM produced bilateral functional deficits in some of the animals and at higher doses (>10 mM), increased startle responses and extensor tone (A). These effects were not seen in saline controls, at lower db-cAMP doses (1 mM), or with a high dose (250 mM) of an alternative cAMP analog, 8-bromo cAMP. Similar to cortical application, tissue damage and micro-hemorrhages beyond the application site of db-cAMP (>1 mM) were found (B–D). The size of the original spinal lesion size was not affected by the application of db-cAMP (E).