Figure 5.
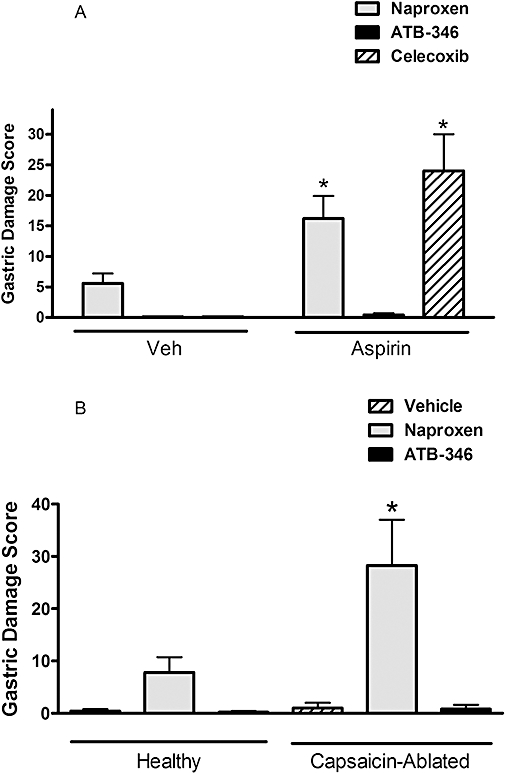
ATB-346 spares the stomach of injury in circumstances in which gastric mucosal defence is impaired. (A) Administration of aspirin at a dose that itself did not cause detectable gastric damage (10 mg·kg−1) resulted in a significant (*P < 0.05; anova and Dunnett's Multiple Comparison test) increase in the severity of gastric damage when co-administered with naproxen (60 µmol·kg−1) or celecoxib (30 µmol·kg−1), but not with ATB-346 (60 µmol·kg−1). (B) Abalation of sensory afferent nerves by neonatal capsaicin treatment resulted in a significant increase (*P < 0.05; Student's t-test) in the severity of naproxen-induced gastric damage, but an equimolar dose (60 µmol·kg−1) of ATB-346 did not cause significant gastric damage in capsaicin-ablated rats. Each group consisted of five to six rats. ATB-346, 2-(6-methoxy-napthalen-2-yl)-propionic acid 4-thiocarbamoyl-phenyl ester; Veh, vehicle.
