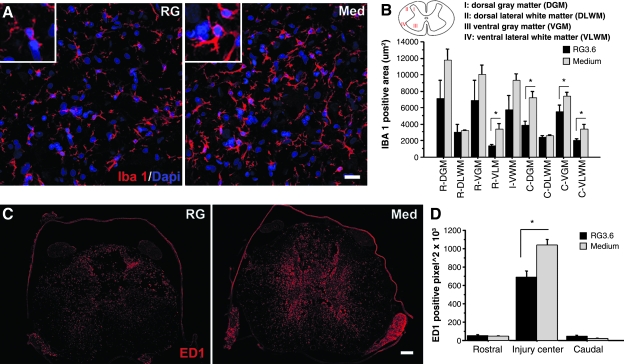
FIG. 1.
Radial glia transplantation reduces neuroinflammation. Microglia were immunolabeled and quantitated by Iba-1 antibody at 7 days post-SCI (A,B). Similar numbers of Iba-1-positive cells were observed in RG3.6 cells (RG) and medium (Med)–treated spinal cords. Microglia in RG3.6-treated spinal cord displayed ramified morphology with thin processes and small cell body (left inset in A). In vehicle medium controls, microglia displayed reactive morphology with thickened processes and hypertrophied cell body (right inset in A). Iba-1 expression was quantitated in injured spinal cords that contained injury epicenter and its adjacent rostral and caudal segments. Four regions were quantitated in each cross section (illustrated in B). RG3.6-treated spinal cords showed significantly lower Iba-1 expression than medium controls (B). Macrophages and activated microglia were immunolabeled and quantitated by ED1 antibody at 14 days post-SCI (C,D). ED1 expression was quantitated in serial sections of injury epicenter (5 mm) and adjacent segments (rostral and caudal 5 mm). RG3.6 transplants significantly reduced ED1 expression at the injury center (D). Scale bar = 20 μm (A), 200 μm (C). Data represent mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 (B), *p < 0.01 (D), t-test.