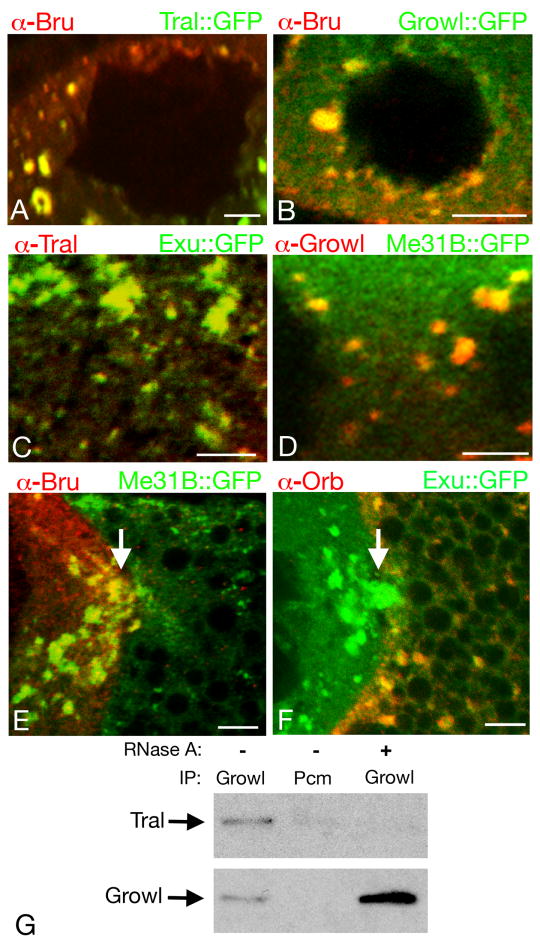
Fig. 2. Sponge body composition and remodeling.
Panels A-D show portions of nurse cells from stage 7 egg chambers. For panels A and B, Bru (red) was detected by immunostaining, and Tral∷GFP (A) and Growl∷GFP (B) (both green) were detected by GFP fluorescence. In each case Bru and the GFP fusion protein are both enriched, and colocalize, in sponge bodies. The circular regions devoid of staining are nurse cell nuclei. For panels C and D the endogenous Tral (C) and Growl (D) proteins were detected by immunostaining (red), with GFP fusion proteins to mark sponge bodies (Exu∷GFP in C, Me31B∷GFP in D). Both Tral and Growl are highly enriched in sponge bodies. Regions devoid of staining in D are portions of nurse cell nuclei. Panel C does not include a nurse cell nucleus, but Tral is not nuclear (Wilhelm et al., 2005).
Panels E and F show portions of stage 9 egg chambers including the boundary between the oocyte (at right) and a nurse cell (at left). In E, Bru (red) is present at high levels in the nurse cell sponge bodies (the arrow shows an example), but is almost completely undetectable in the oocyte sponge bodies, most of which are small and dispersed in this egg chamber. The sponge bodies are marked with Me31B∷GFP. In F, Orb (red) cannot be detected in the nurse cell sponge bodies, but is present at high levels in the oocyte sponge bodies. The sponge bodies are marked with Exu∷GFP. The positions of ring canals connecting the nurse cells and oocytes are indicated by arrows. Scale bars are 10 μm in all panels.
Panel G shows the RNA dependent interaction between Tral and Growl. Immunoprecipitations were performed out of ovarian extracts using Growl or a negative control antibody (Pcm) in the presence or absence of RNase A. Western blots of the immunoprecipitated proteins were performed using anti-Tral antibody (top panel) or Growl antibody (bottom panel).