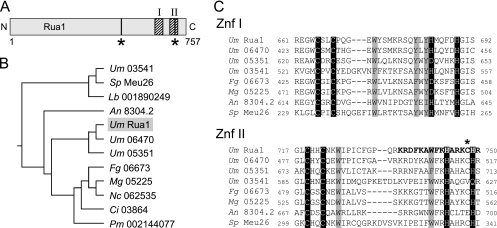
FIG. 1.
Domain organization of the transcription factor Rua1. (A) Scheme of the domain organization of Rua1. The two C-terminal zinc finger domains are indicated by hatched areas. Predicted nuclear localization motifs are marked by vertical bars and asterisks. (B) Database comparison of the C-terminal region reveals that Rua1 is related to a yet uncharacterized subfamily of fungal proteins. The tree was constructed with CLUSTALW. The GenBank accession numbers are as follows: for U. maydis (Um) 03541, XP_759688; for Schizosaccharomyces pombe (Sp) Meu26, BAB60877; for Lacaria bicolor (Lb) 001890249, XP_001890249; for A. nidulans (An) 8304.4, CBF80270; for U. maydis (Um) Rua1, XP_762605; for U. maydis (Um) 06470, XP_762617; for U. maydis (Um) 05351, XP_761498; for Fusarium gramineum (Fg) 06673, XP_386849; for Magnaporthe grisea (Mg) 05225, XP_359552; for Neurospora crassa (Nc) 062535, XP_963086; for Coccidioides immitis (Ci) 03864, XP_001244423; and for Penicillium marneffei (Pm) 002144077, XP_002144077. (C) Sequence alignment of both Rua1 zinc finger domains (ZnF I and ZnF II). The Cys and His residues predicted to be involved in coordination of zinc are shaded in black. Highly conserved amino acids are shaded in gray. The C-terminal nuclear localization motif overlaps with the Znf II sequence (bold letters); the amino acid exchanged in the rua1C747R mutant strain is marked with an asterisk.