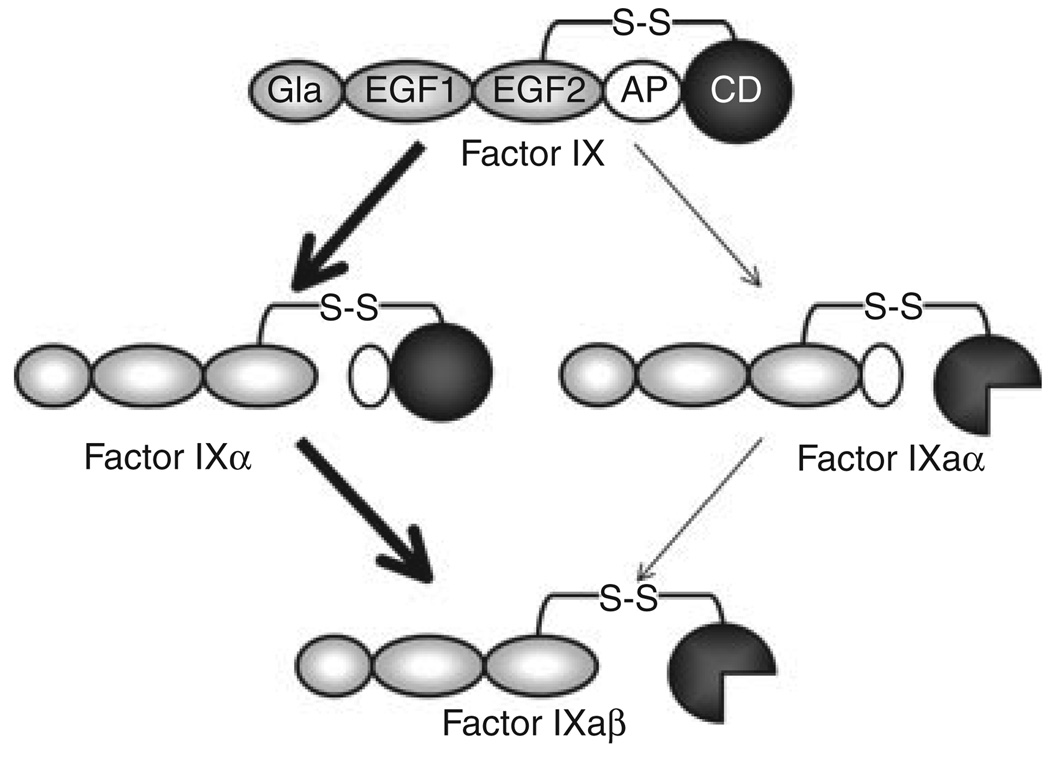
Fig. 4.
Factor IX Activation. Factor (F) IX is converted to FIXaβ by cleavage after Arg145 and Arg180, releasing the activation peptide (white oval) that connects the catalytic domain (CD) to the non-catalytic light chain (Gla and EGF domains). FVIIa/TF initially cleaves FIX after Arg145 to form the intermediate FIXα, with subsequent cleavage after Arg180 forming FIXaβ (bold arrows). The active catalytic domain of FIXaβ is indicated by the three-quarter circle. During this reaction, FIXα accumulates prior to formation of FIXaβ. FXIa also cleaves FIX initially after Arg145, however, no FIXα accumulates, suggesting that subsequent cleavage after Arg180 is relatively rapid. Activation of FIX by initial cleavage after Arg180 (through FIXaα) is a minor reaction (thin arrows).