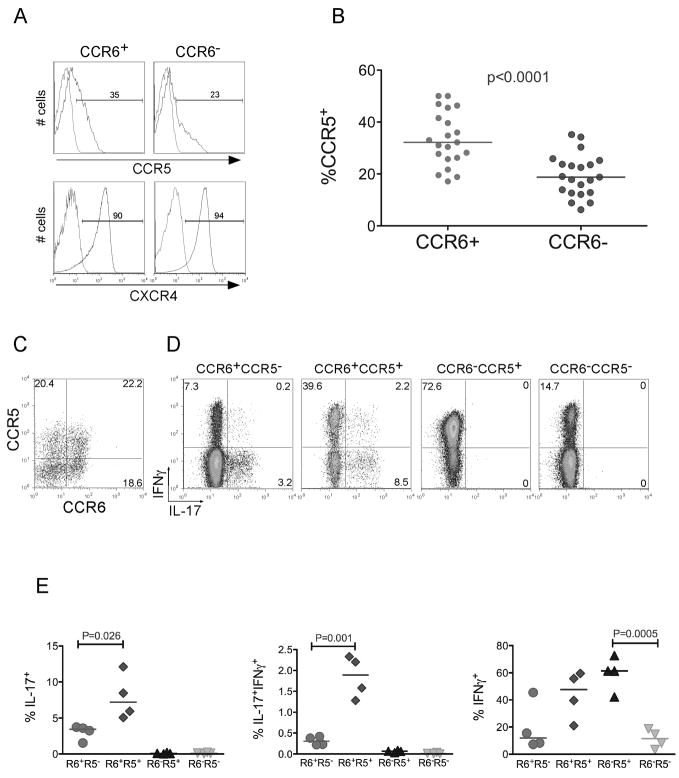
Figure 1. CCR5 segregates Th17 cells into IFNγ−IL-17+ and IFNγ+IL-17+.
(a) Resting CD4+, CD45RO+, CCR6+ or CCR6− T cells were purified as described (methods) and stained with CCR5-PE or CXCR4-PerCP-cy5.5 antibodies (blue) or isotype-matched controls (red). (b) Percent of memory CCR5+ cells in CD4+ cells stained for CCR5 and CCR6. Each circle is representative of one adult healthy donor. (c) Resting memory CD4+ T cells were stained with CCR6-biotin and CCR5-PE (d) Stained cells in (c) were sorted into four memory (CD45RO+) subsets: CCR6+CCR5−, CCR6+CCR5+, CCR6−CCR5+, and CCR6−CCR5−. To detect IL-17 and IFNγ producing cells; we activated sorted subsets using PMA, Ionomycin and Golgi stop. Cells were fixed, permeabilized and stained with IFNγ-PE-cy7 and IL-17-FITC antibodies. An isotype-matched control did not show any background staining (data not shown). (e) Percent of IL-17+, IFNγ+ and IFNγ+IL-17+ in memory CCR6+CCR5−, CCR6+CCR5+, CCR6−CCR5+, and CCR6−CCR5− T cell subsets. Each symbol represents one adult healthy donor. P values were calculated using the Two-Sample Student’s t-test.