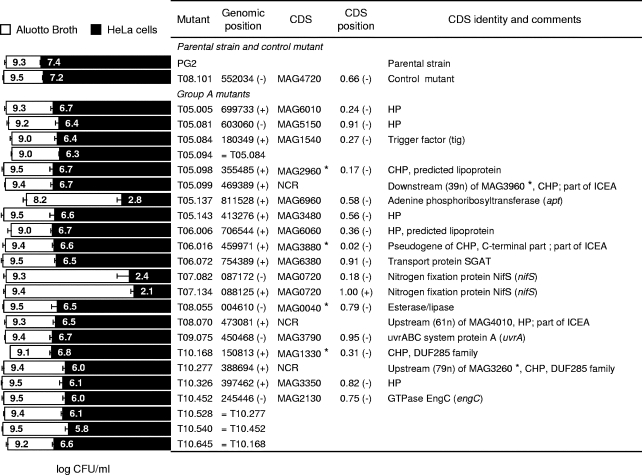
FIG. 2.
Characterization of M. agalactiae mutants displaying altered growth in cell culture. Mutants were designated according to transformation and clone numbers (e.g., T05.081 designates clone 81 isolated from transformation T05). PG2 and T08.101 refer to the parental strain and the control mutant, respectively. Group A mutants were selected from the mutant library by high-throughput screening on HeLa cells, as described in the Results section. Mycoplasma titers (log CFU/ml) at 48 h in Aluotto broth (open bars) and at 72 h in cell culture (solid bars) are compared. The data are the means of at least three independent assays. Standard deviations are indicated by error bars. Transposon insertion sites were determined by direct sequencing of genomic DNA, and their positions were defined based on the published sequence (NC_009497). The orientation of the inserted sequences is indicated in parenthesis. Mutants sharing an identical insertion are indicated. CDSs found disrupted in M. agalactiae mutants are indicated by the mnemonic codification (45). Noncoding regions are indicated. CDSs involved in horizontal gene transfer between M. agalactiae and mycoplasmas of the mycoides cluster (45) are designated by asterisks (*). For each CDS, the relative position and orientation of the inserted transposon are indicated (CDS position). Hypothetical proteins (HP) have no homologs outside the M. agalactiae species. Conserved hypothetical proteins (CHP) share sequence similarity with proteins of unknown function identified in mollicutes or other bacteria. Several insertion sites mapped within a 20-kb locus that contains a vestige of an integrative conjugative element (ICEA).