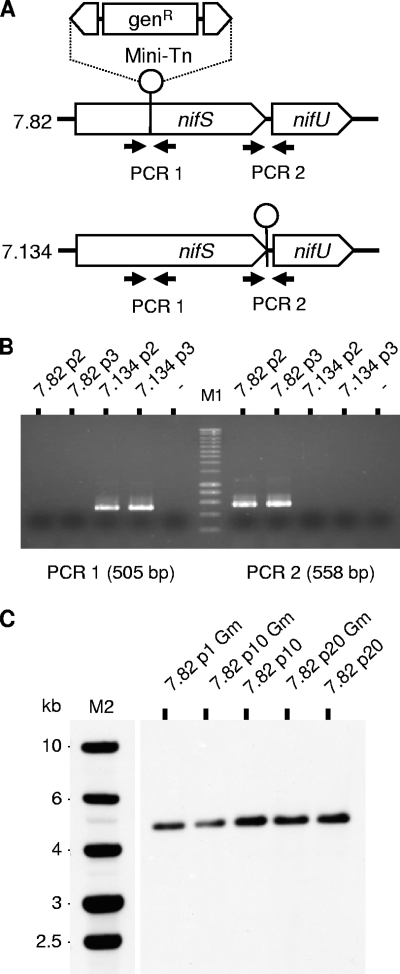
FIG. 3.
Clonality and stability of M. agalactiae NIF mutant populations. (A) The genomic regions surrounding the transposon insertion site in mutants T07.82 and T07.134 were analyzed by PCR amplification to detect the presence of contaminating transposon-free sequences. PCR1 and PCR2 were performed using the primer pair 86768F (5′-TCAGCCGACATTATTCATGG-3′) and 87272R (5′-CACCGGCTTTTAATTTTTGC-3′) and the pair 88037F (5′-AGGGTTTCGCTAGGGGTTTA-3′) and 88595R (5′-CTGTGCGCGCTTACAAAGTA-3′), respectively. (B) The PCR1 product (505 bp) amplified from mutant T07.134 populations at passages 2 (7.134p2) and 3 (7.134p3) was not detected upon amplification of the corresponding populations of mutant T07.82 (7.82p2 and 7.82p3). The opposite result was observed for the PCR2 product (558 bp). These negative results suggest the absence of detectable contaminating sequences in all the populations tested. M1, molecular weight markers (SmartLadder; Eurogentec). (C) Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA derived from NIF mutant T07.82 (7.82) at passages 1, 10, and 20 in selective (Gm) or nonselective medium. Genomic DNA was digested by HindIII and Southern blot hybridized with DIG-labeled amplicons derived from plasmid pMT85. M2, molecular weight markers (1 Kb DNA ladder; Promega).