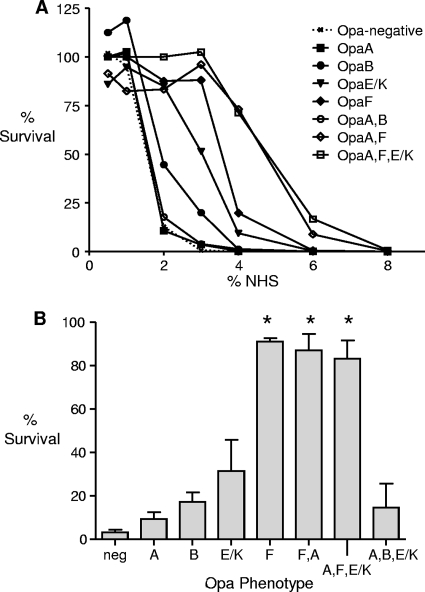
FIG. 5.
Expression of some FA1090 Opa proteins is associated with increased resistance to NHS. The bactericidal activity of NHS was tested using different Opa variants of the serum-sensitive derivative FA1090F62por5-8. (A) Plot of the level of survival of each variant tested versus the dilution of NHS tested. The representative data from several independent assays show that there was an increase in the 50% bactericidal titer compared to the 50% bactericidal titer for Opa− variants for gonococci that express OpaB, OpaE/K, OpaF, OpaA,F, and OpaA,F,E/K but not for variants that express OpaA or OpaA,B. The 50% bactericidal titers were 1.8% (Opa−, OpaA, and OpaA,B), 2.2% (OpaB), 3.4% (OpaE/K), 3.8% (OpaF), and ca. 5.1% (OpaA,F and OpaA,F,E/K). (B) Levels of survival of different Opa variants following incubation in 3% NHS. The results are expressed as the average levels of survival when data from at least three independent experiments were combined. The error bars indicate the standard errors of the means, and the asterisks indicate that there was a significant difference (P < 0.0001). The level of survival was calculated by dividing the number of CFU recovered from wells with NHS by the number of CFU recovered from wells with the same concentration of HI-NHS and multiplying by 100.