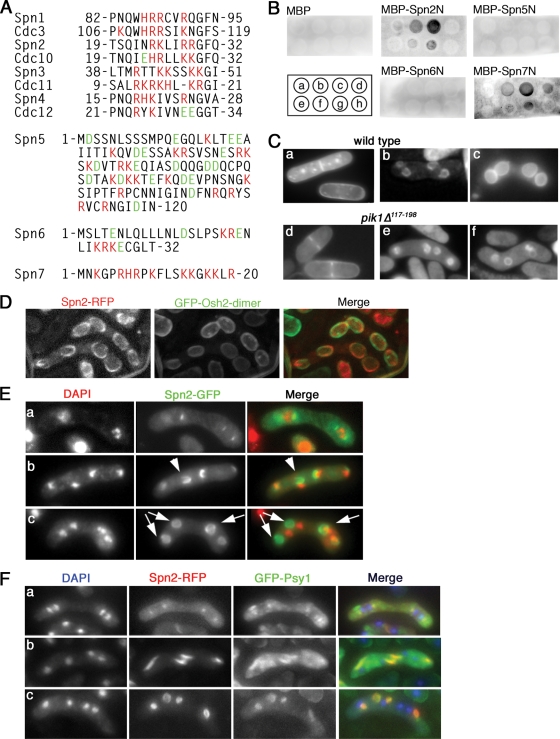
FIG. 11.
Interaction of Spn2 and Spn7 with phosphoinositides. (A) Clusters of basic amino acids near the N termini of some septins. Spn1 to Spn4 were aligned with their S. cerevisiae orthologues to show the conservation of this aspect of septin structure. For Spn5 to Spn7 (which do not have clear orthologues), the N-terminal sequences are shown without comparisons. Red, basic amino acids; green, acidic amino acids; numbers, amino acid positions relative to the N termini. (B) Binding of Spn2 and Spn7 to PtdIns(4)P and PtdIns(5)P in a protein-lipid overlay assay. Phosphoinositide spots on a nitrocellulose membrane were incubated with purified MBP or the indicated MBP fusion proteins (see Materials and Methods). The fusion proteins contained N-terminal fragments (136 to 200 amino acids in length) of the respective septin. Bound proteins were detected using an anti-MBP antibody. The positions of lipid spots were as follows: a, PtdIns; b, PtdIns(4)P; c, PtdIns(5)P; d, PtdIns(4,5)P2; e, PtdIns(3)P; f, PtdIns(3,4)P2; g, PtdIns(3,5)P2; and h, PtdIns(3,4,5)P3. Small, uneven signals (such as seen for MBP-Spn2N [g]) appear to be nonspecific background because they were independent of the dose of lipid on the membrane (not shown). (C) Presence of PtdIns(4)P in normal FSMs and in the abnormal FSMs of a pik1 mutant. Wild-type strain THP18 (a to c) and pik1Δ117-198 strain MO599 (d to f) were transformed with pREP41(GFP-PHOsh2-dimer), grown in EMM-plus-thiamine liquid medium overnight, shifted to EMM liquid medium (a and d) or to an SSA plate (b, c, e, and f) for 12 h, and examined by fluorescence microscopy. (D) Distinct localizations of septin structures and PtdIns(4)P. Strain MO815 (spn2+-mRFP) was transformed with pREP41(GFP-PHOsh2-dimer) and treated as in panel C. Maximum projections of deconvoluted images are shown. (E) Formation of septin rings that do not surround the nuclei in sporulating pik1 mutant cells. Strain MO599 (pik1Δ117-198) was transformed with plasmid pAL(spn2-GFP), sporulated, and examined by fluorescence microscopy. Cells in metaphase (a) and anaphase (b) and after completion of meiosis II (c) are shown. Arrowhead, a horseshoe-shaped structure that does not surround the adjacent nucleus (seen at 17 to 36% of nuclei at this stage in three independent experiments); arrows, seemingly completed septin rings that do not surround the adjacent nuclei (seen at 76 to 89% of nuclei at this stage in three experiments). (F) Association between abnormal septin rings and abnormal FSMs in pik1 mutant cells. Strain MO832 (pik1Δ117-198 spn2+-mRFP GFP-psy1+) was sporulated and examined by fluorescence microscopy.