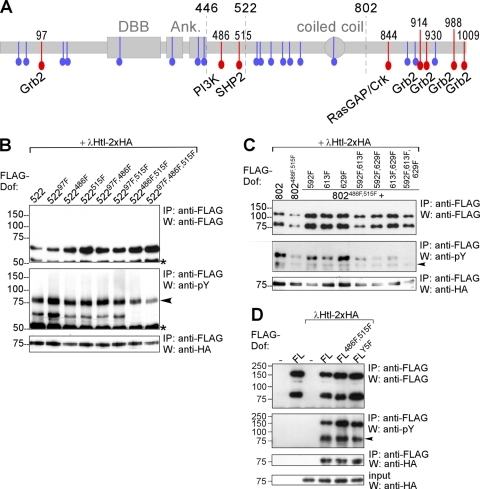
FIG. 1.
Mapping of phosphorylated tyrosines in Dof. (A) Schematic representation of the Dof protein. Two gray boxes and one oval represent the Dof-BCAP-BANK (DBB) domain, the two ankyrin repeats (Ank), and the coiled coil region. All tyrosines are marked in color; red highlights the tyrosines located within consensus motifs for binding sites for the indicated signaling molecules. The amino acid positions of these tyrosines are indicated on top of the scheme. Tyrosines that do not form part of a known consensus motif are marked in blue. Breakpoints of the Dof deletion constructs used or cited in this study—after amino acid positions 446, 522, and 802—are marked with dashed lines. (B to D) FLAG epitope-tagged mutant Dof constructs were expressed together with an activated form of HA-tagged Heartless (λHtl-2xHA) in S2 cells. FL, full-length Dof; 802 and 522, Dof constructs truncated after amino acid positions 802 and 522, respectively. Protein complexes were immunoprecipitated (IP) from whole-cell lysates using an antibody against the FLAG epitope tag of the Dof constructs. The precipitated FLAG-Dof and the coprecipitating λHtl-2xHA proteins were detected on Western blots (W) using antibodies directed against FLAG and HA. In addition to a protein of approximately the size predicted for each of the mutant FLAG-Dof constructs, for the FL and 802 Dof proteins the FLAG antibody also detects a smaller fragment of about 75 kDa representing an N-terminal cleavage product of Dof (see also reference 41). This additional protein band is absent in 522 constructs, because the cleavage site lies C-terminal to the position of truncation. The phosphorylation state of mutant Dof proteins was determined by a phosphotyrosine antibody. This antibody also recognizes the tyrosine-phosphorylated λHtl-2xHA construct, which interacts with Dof and therefore coprecipitates; these bands are marked with a black arrowhead. The asterisk marks the IgG heavy chain of the FLAG antibody. (B) FLAG-Dof constructs containing the first 522 amino acids of Dof with combinations of the Y to F point mutations at positions 97, 486, and 515 were coexpressed with λHtl-2xHA. (C) FLAG-Dof constructs containing the first 802 amino acids with combinations of Y to F point mutations at positions 486, 515, 592, 613, and 629 were coexpressed with λHtl-2xHA. As a positive control for phosphorylation, a Dof construct containing amino acids 1 to 802 without further mutations was used. (D) Full-length FLAG-Dof constructs with combinations of Y to F point mutations at positions 486, 515, 597, 613, and 629 (FLY5F, all of these five tyrosines mutated) were coexpressed with λHtl-2xHA.