FIG. 3.
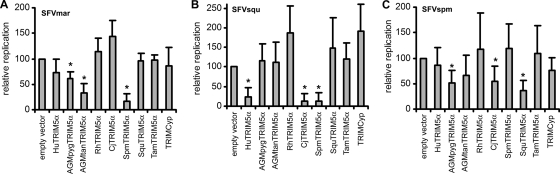
Restriction of NWM SFV infection by TRIM5α and TRIMCyp proteins. Cf2Th cells stably expressing TRIMCyp from owl monkeys or comparable levels of TRIM5α proteins from different primate species or transduced with the empty control vector were infected with SFVmar (A), SFVsqu (B), or SFVspm (C). Cell supernatants were collected 3 or 4 days later and analyzed for RT activity. Values represent the RT level of each virus at 3 to 4 days postinfection relative to that seen in the cells containing the empty vector. Values are the means derived from 5 to 11 different experiments, each performed in duplicate. Error bars represent the standard deviation. Significant reductions in virus replication, determined by using the Bonferroni t test (2) and indicated by a P value of 0.0056, are marked by asterisks. CjTRIM5α (Callithrix jacchus TRIM5α) cDNA was prepared using the following primers: CjTrim-F, 5′-GGGAATTCATGGCTTCCAGAATCCTGGT-3′, and CjTrim-R, 5′-GGAGCGGCCGCATCAAGAGCTTGGTGA-3′. In the process of producing the cDNA, an N-terminal hemagglutinin (HA) epitope tag was added to the encoded CjTRIM5α protein to facilitate detection. Hu, human; Rh, rhesus monkey; AGMpyg, African green monkey (Chlorocebus pygerythrus); AGMtan, African green monkey (Chlorocebus tantalus); Spm, spider monkey; Cj, Callithrix jacchus (common marmoset); Squ, squirrel monkey; Tam, tamarin.