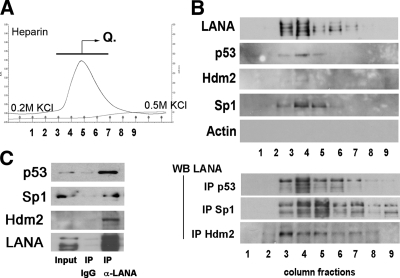
FIG. 2.
Analysis of LANA binding complexes after heparin affinity chromatography. (A) Profiles of the eluted peaks, using wash buffer with 0.2 M KCl (pH 7.9) and a step gradient up to 0.5 M KCl. Traces show total protein based on UV absorption (absorbance units [A.U.]) and absorbance in mS/cm. The bar with the arrow and letter “Q” indicates the fractions that were pooled and subsequently loaded onto a Mono Q column. (B) Components (1 to 9 tubes of continuous fractions) of the elution peak (0.2 M to 0.5 M) were analyzed with Western blotting (WB) and by immunoprecipitation (IP) followed by Western blotting. (C) Immunoprecipitation followed by Western blotting of nuclear extract prior to chromatography. We used rat monoclonal anti-LANA antibody for immunoprecipitation and anti-p53, anti-hdm2, and anti-LANA antibodies as indicated. Components (1 to 9 tubes of continuous fractions) of the elution peak (0.2 M to 0.5 M) were analyzed with Western blotting and by immunoprecipitation assay.