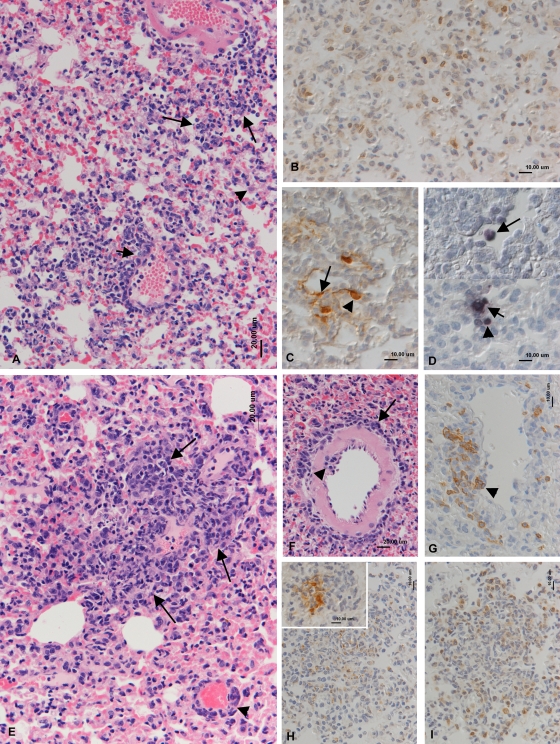
FIG. 2.
Histopathological analysis of lungs at day 7 p.i. (A to D) BALB/c mice. (A) Intense diffuse increased interstitial cellularity and small mononuclear infiltrates (large arrows), activation of type II pneumocytes (arrowhead), and mononuclear infiltration of venous wall (phlebitis; small arrow). HE stain. (B) T cells (CD3+; PAP method) dominate in the interstitial infiltration. (C) Viral antigen (PAP method) is expressed by type I (arrow) and type II (arrowhead) pneumocytes. (D) vtRNA expression (RNA-ISH) in a type II pneumocyte (small arrow), a lymphocyte (arrowhead), and a desquamed alveolar macrophage (large arrow). (E to I) Wood mice. (E) Multifocal granulomatous infiltration (arrows) and perivenous lymphocyte infiltration (arrowhead). HE stain. (F) Artery with emigrating (arrowhead) and perivascular (arrow) lymphocytes. HE stain. (G) B cells (CD45R+; ABC method) dominate in the perivascular infiltrate and are seen rolling and attached to endothelial cells (arrowhead). (H) Staining for lysozyme (PAP method) identifies numerous macrophages in the focal granulomatous infiltrates. (Inset) Viral antigen is detected (PAP method) in macrophages within the granulomatous infiltrates. (I) T cells (CD3+; PAP method) represent the dominant lymphocyte population in granulomatous infiltrates.