FIG. 2.
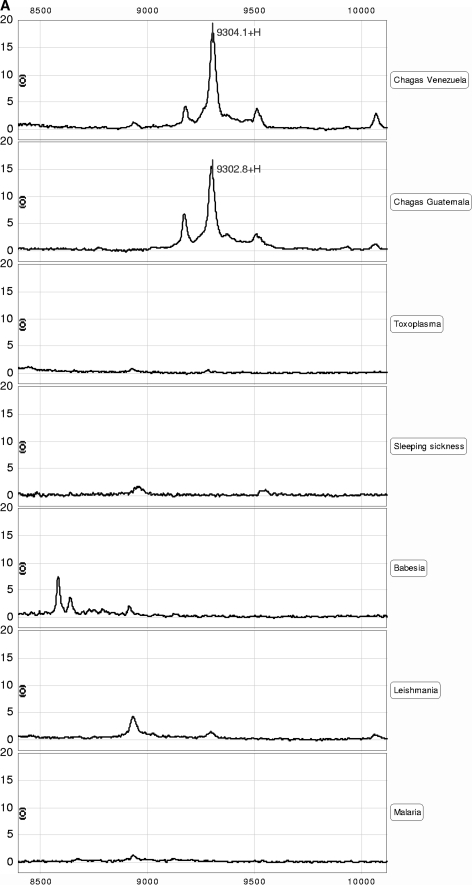
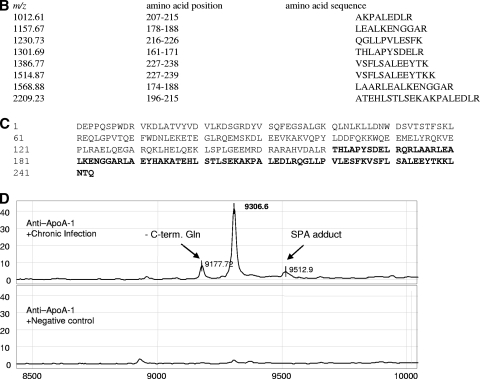
SELDI-TOF MS identification of the 9.3-kDa candidate biomarker. (A) Representative spectral view of IMAC spectra of the Chagas' disease sera and the parasite controls (Toxoplasma, African sleeping sickness, Babesia, Leishmania, and malaria). The 9.3-kDa protein, detected in Chagas' disease but not other diseases, is shown. (B) The 9.3-kDa protein was purified from serum samples by anion-exchange chromatography followed by reverse-phase chromatography and, finally, 16% Tricine SDS-PAGE. Coomassie blue-stained bands were extracted and reprofiled on NP20 arrays. A band corresponding to the 9.3-kDa protein was digested in solution with trypsin, and the digest was analyzed by tandem mass spectrometry. Eight peptides were identified as components of a C-terminal fragment of ApoA1. (C) Amino acid sequence of human ApoA1. The amino acid sequence encompassed by the peptides identified by tandem mass spectrometry is highlighted in bold. The calculated molecular mass for the highlighted sequence is 9,306.59 Da. (D) Immunocapture of C-terminal fragments from serum samples, using rabbit polyclonal antibody against ApoA1.