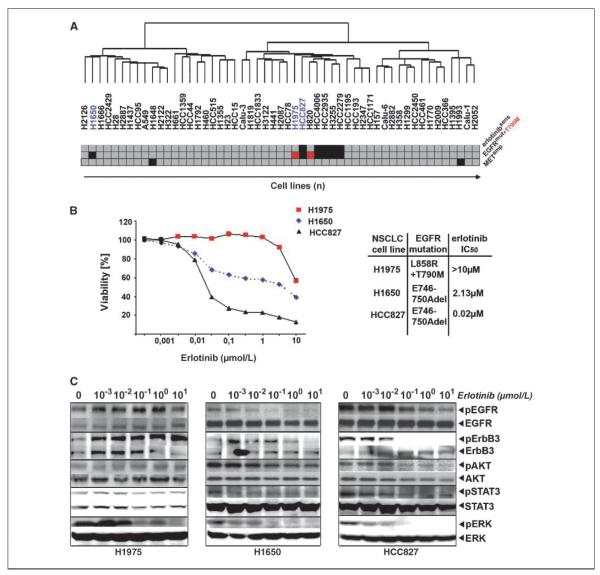
Figure 1.
An EGFR independence signature in H1650 cells. A, hierarchical clustering of 53 NSCLC cells according to gene expression. Erlotinib sensitivity (IC50 < 1 μmol/L, red; IC50 > 1 μmol/L, gray) and EGFR mutations (EGFR-mutant, black; T790M, red; EGFR wild-type, gray) as well as MET amplification (black). B, left, cellular viability as a function of erlotinib dose for all three cell lines studied. Right, mutation status and IC50 values. C, cells were treated with different doses of erlotinib. Activation of EGFR and downstream signaling pathways was determined by analyzing the amount of phosphorylated versions of the respective proteins in comparison with their total levels using phosphorylation-specific antibodies.