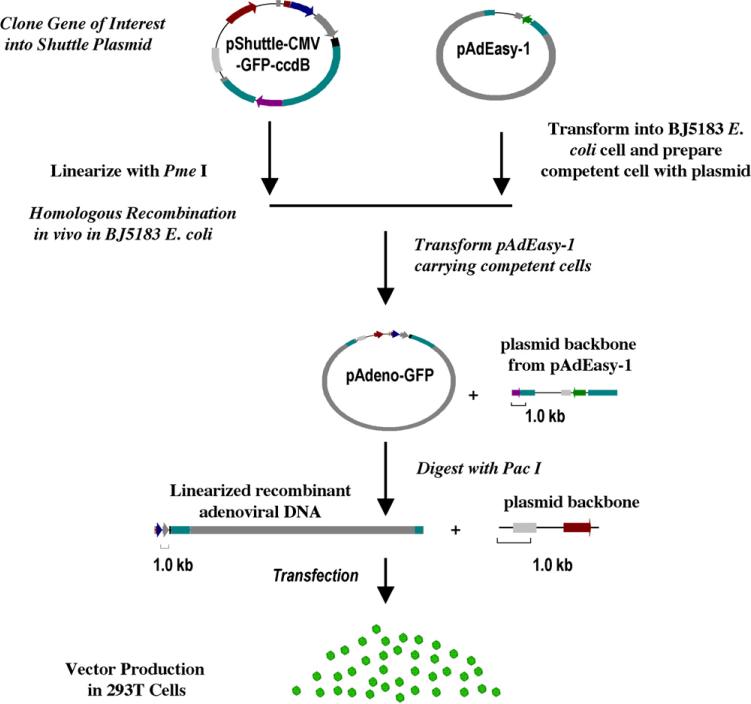
Fig. 4.
Schematic outline of the optimized recombinant adenovirus vector system through plasmid recombination in E. coli cells. First, the gene of interest is cloned into a shuttle vector, such as the illustrated pShuttle-CMV-GFP-ccdB as illustrated; Second, the resulting plasmid is digested with a restriction enzyme, Pme I(ccdB-containing plasmids can also be used in supercoiled form). For shuttle plasmids not containing the ccdB gene, linearized DNA is further treated with CIP and Taq DNA polymerase; Third, competent BJ5183 E. coli cells carrying pAdEasy-1 is transformed with linearized plasmid DNA; Fourth, the recombinant adenoviral plasmid is digested with Pac Ito expose the adenoviral inverted terminal repeats (ITR) and transfected into a 293T packaging cell line. Infectious recombinant adenoviral vector particles are obtained from the transfected cells and amplified by infecting fresh 293T cells.