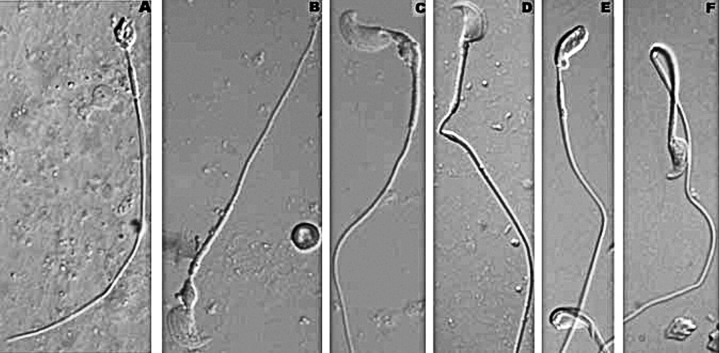
FIG. 4.
The DIC imaging of testicular, caput, and cauda epididymal spermatozoon. A) Typical testicular sperm from Ppp1cc−/− mouse. Note rounded deformed head and the mitochondrial sheath abbreviated at both ends. B) Typical testicular sperm from rescue mouse containing a hook-shaped head, a cytoplasmic remnant at the head/connecting piece junction, a distally shortened mitochondrial sheath, and a straight flagellum. C) Testicular sperm from rescue mouse showing gross similarities to sperm in B but displaying non-hairpin bending at the head/connecting piece junction and in the principal piece. Note the distally shortened mitochondrial sheath, leaving a small gap between the mitochondrial sheath and the beginning of the principal piece. D) Rescue sperm from the caput epididymis. Note ∼90° sharp bend at a gap in the mitochondrial sheath near the distal end of the midpiece. E) Cauda epididymal sperm from rescue mouse. Note the gap in the mitochondrial sheath near the head/connecting piece junction of upper sperm, as well as the head/connecting piece junction hairpins, where the heads appear to be engulfed in cytoplasm with the proximal midpiece. F) Cauda epididymal sperm exhibiting hairpin bend at the midpiece/principal piece junction. All sperm were viewed at 100× magnification.