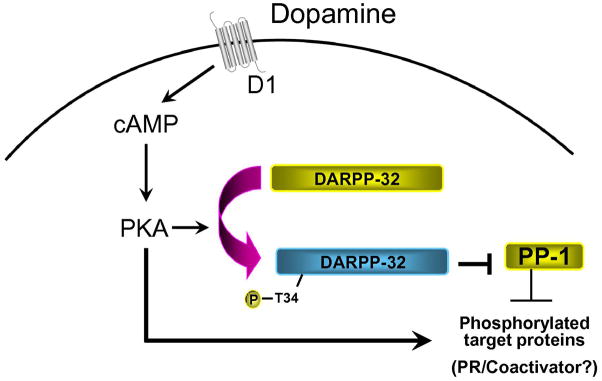
Fig. 5.
Mechanism of dopamine action in the hypothalamus. Dopamine acting via D1 receptor subtype stimulates an increase in cAMP levels and PKA activity, leading to enhanced phosphorylation of the neuronal phosphoprotein DARPP-32 on Thr34. Phosphorylation of DARPP-32 converts the phosphoprotein to a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase 1 (PP-1). Phosphatase inhibition leads to increased kinase activity and increased phosphorylation of target proteins including PR and/or coactivators.