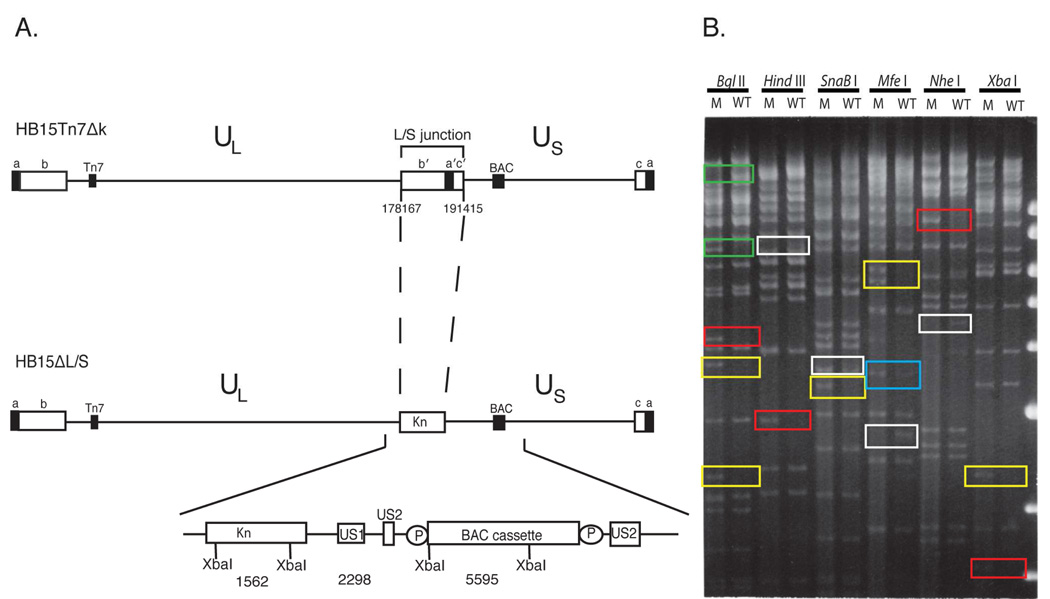
Figure 1.
Deletion of the L/S junction from the HCMV genome. (A) The P genome isomer of parental virus HB15Tn7Δk is shown with ab and b′a′ repeats flanking UL and a′c′ and ca repeats flanking US, the attTn7 site (Tn7) inserted in UL, and the BAC origin cassette (BAC) inserted in US. Below is shown the HB15ΔL/S genome in which Kn replaces b'a'c'. Sequences deleted from HB15Tn7Δk are indicated using nucleotide numbers that correspond to the AD169 genome sequence (Chee et al., 1990). The Kn - BAC origin region is expanded below to show the predicted sizes (bp) of diagnostic XbaI fragments, direct duplications of US2 sequences that allow excision of the BAC origin by homologous recombination, and LoxP sites (P) flanking the BAC origin. (B) Restriction analyses of HB15ΔL/S and HB15Tn7Δk. Virion DNAs from HB15ΔL/S (M) and HB15Tn7Δk (WT) were digested with the indicated restriction enzymes. The resulting DNA fragments were separated on 0.7% agarose and visualized with ethidium bromide and UV light. Colored boxes indicate fragments that are lost or created in HB15ΔL/S by deletion of b'a'c' (green), fragments that are unique to HB15ΔL/S by virtue of the Kn insertion (red), fragments that indicate retention of the BAC cassette in HB15ΔL/S (yellow), IS isomer S-terminal fragments missing from HB15ΔL/S (white), and a P isomer S-terminal fragment that is half-molar in HB15Tn7Δk and equi-molar in HB15ΔL/S (blue). The positions and sizes (kb) of DNA size markers are shown on the right.