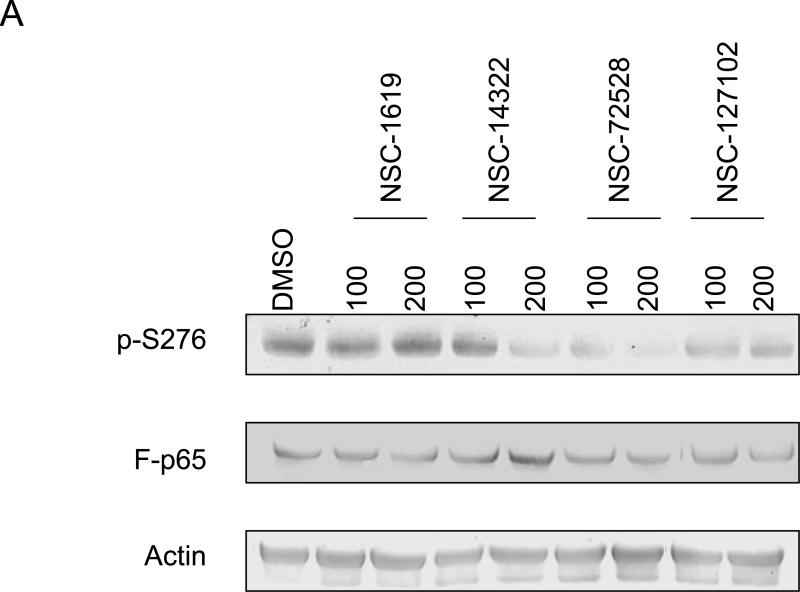
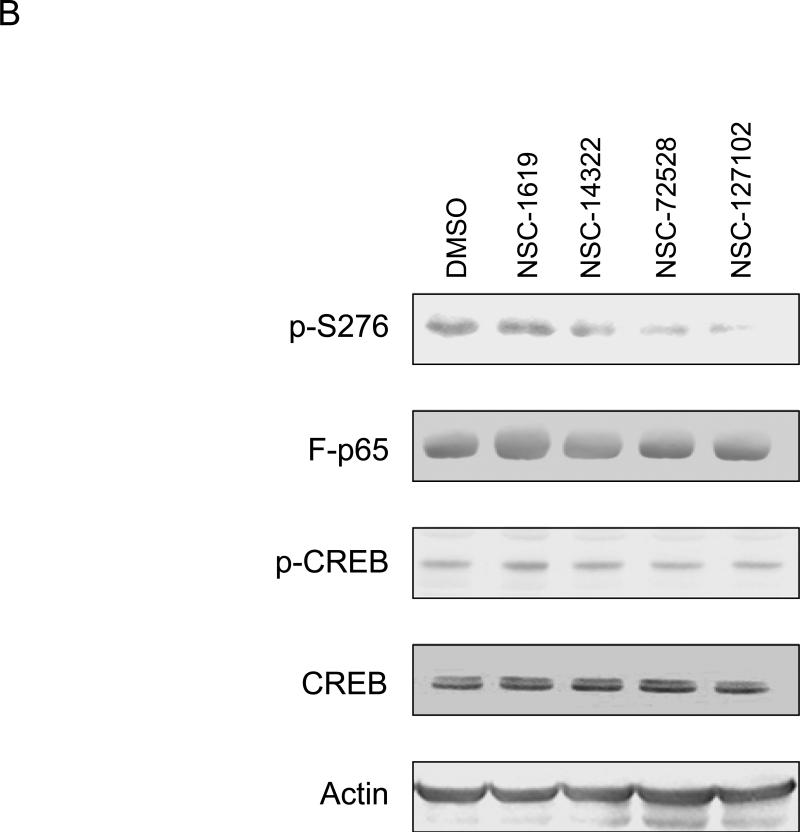
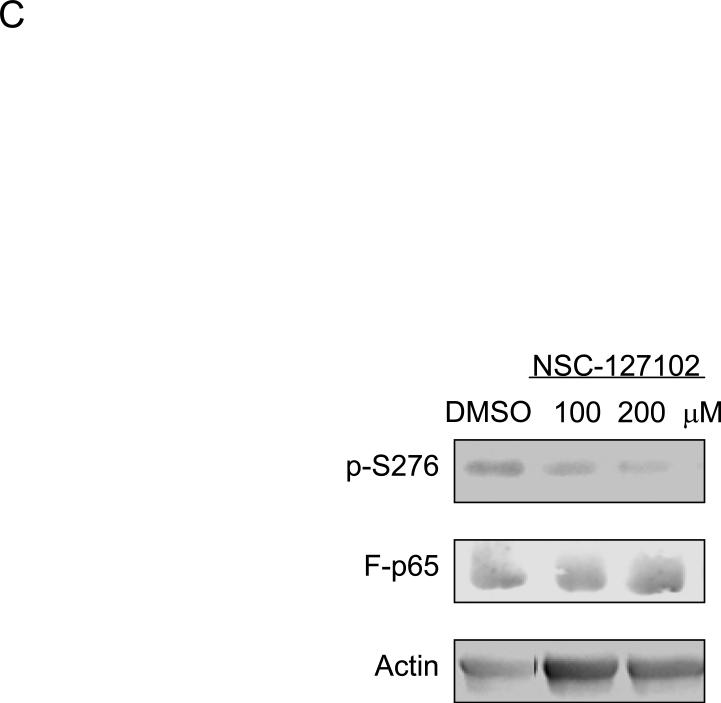
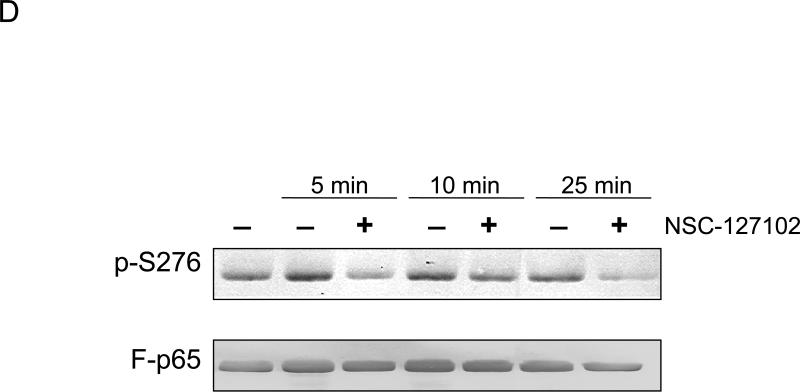
Fig. 2.
NSC-127102 inhibits serine 276 phosphorylation of p65. (A) HepG2 hepatoma cells were infected with an adenovirus expressing flag epitope tagged p65 (F-p65) for 24 h. Cells were subsequently treated for another 24 h with 100 or 200 μM of the compounds obtained from the NCI/DTP. DMSO served as vehicle control. F-p65 was immunoprecipitated using anti-Flag-agarose and immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblot using antibodies that specifically recognize p65 or p65 phosphorylated on serine 276 (p-S276). Prior to flag-agarose immunoprecipitation, whole cell lysates were prepared and analyzed by immunoblot analysis for β-actin to confirm that all lanes were equally loaded. (B) HepG2 hepatoma cells were infected with an adenovirus expressing F-p65, as described in panel A and subsequently treated with 100 μM NSC-1619, NSC-14322, NSC-72528, or NSC-127102 for 24h. Whole cell lysates prior to immunoprecipitation were also prepared. Immunoblot analysis for p65, p-S276, CREB, CREB phosphorylated on serine 133, and β-actin, as a loading control, was performed. (C) Experiments performed in HepG2, as described in panel A, were repeated in MDA-MB-231 cells. MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with 100 or 200 μM NSC-127102 for 24 h, and immunoblot analysis for p65, p-S276 and β-actin was performed. (D) HepG2 cells were pre-treated with DMSO or 100 μM NSC-127102 for 24 h. Cells were subsequently treated with 40 ng/ml TNF-α for 5, 10, and 25 min. F-p65 was immunoprecipitated using flag-agarose and immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblot using antibodies that specifically recognize p65 or p65 phosphorylated on serine 276 (p-S276).