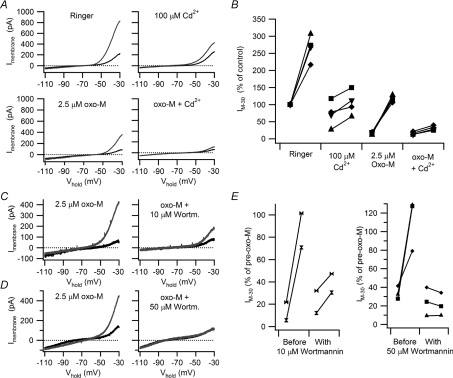
Figure 7. Cd2+ and wortmannin inhibit the activity-dependent enhancement of IM.
A, I–V relations from an experiment on a B neuron where the increase in IM produced by a 40 s, 10 Hz train of action potentials was attenuated by 100 μm Cd2+ and almost entirely eliminated after partial IM suppression with 2.5 μm oxo-M. B, data from four cells that all behaved like the cell in panel A. In these plots, IM was normalized to the resting level in Ringer solution prior to any stimulation. C and D, I–V relations illustrating how the effect of 40 s, 10 Hz train of action potentials was reduced in 10 μm wortmannin (C) and elimated in 50 μm wortmannin (D) in cells where IM had been partially suppressed with 2.5 μm oxo-M. E, similar effects of oxo-M plus wortmannin were observed in 5 of 5 neurons where activity-dependent increases in IM were reduced or eliminated.