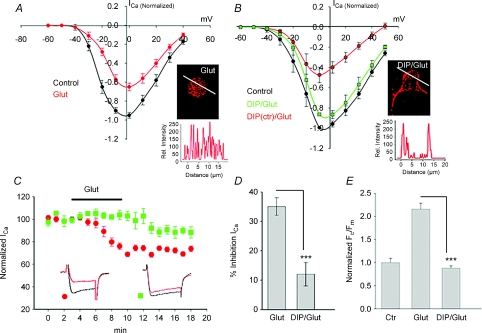
Figure 5. Correlation between channel internalization and inhibition of L-type current by glutamate.
A, I–V relationships of whole-cell L-type ICa recorded from ganglion cells in salamander retinal slices from a holding potential of −60 mV to +40 mV in 10 mV increments in control, and in the presence of 100 μm glutamate. B, the inhibitory effect of glutamate on ICa was attenuated in cells pre-treated with DIP, but not with its scrambled analogue (DIPctr). Immunofluorescence confocal images of cells under indicated conditions are illustrated in insets. C, time course of the normalized peak ICa (mean ±s.e.m.) recorded with the patch pipette containing either DIP or its scrambled inactive form (DIPctr) in the presence of glutamate in the bath solution. The bar graphs summarize the effect of DIP on glutamate-induced inhibition of ICa (D), and internalization of Cav1.3 (E). Values represent mean ±s.e.m. (n= 7–16, P < 0.05).