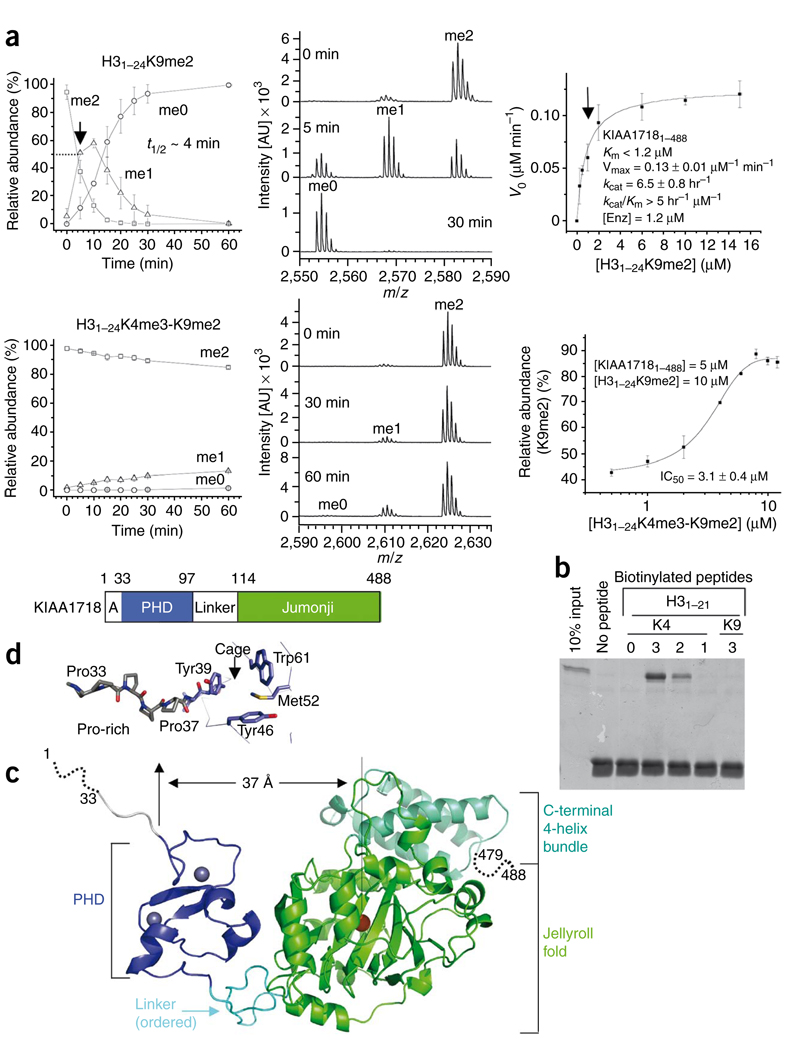
Figure 2.
KIAA1718 PHD binding of H3K4me3 inhibits its jumonji domain activity targeting H3K9me2. (a) Effect of H3K4me3 on the demethylation of H3K9me2 by KIAA1718. Left panels show progression of demethylation as a function of reaction time. Middle panels show representative mass spectra at various time points. Right top panel shows kinetics of KIAA1718 on substrate H31–24K9me2. KM is estimated to be less than 1.2 µM (indicated by an arrow), which is the amount of enzyme used to generate sufficient fluorescence signal. Right bottom shows the IC50 value of H31–24K4me3-K9me2 peptide [I] on H31–24K9me2 [S] demethylase activity of KIAA1718 [E]. The relative abundance of the substrate [S] was measured after eight minutes incubation at 37 °C by adding varying amounts of [I] to the reaction mixture. No demethylation of the doubly methylated peptide occurred. (b) Peptide pulldown assays with peptides H31–21 that were unmodified or mono-, di- or trimethylated (1, 2 or 3) at H3K4 or H3K9 using a GST-tagged PHD domain of KIAA1718. (c) KIAA1718 contains four segments: a disordered alanine-rich sequence followed by a stretch of prolines, a PHD domain (blue) containing two zinc metals (gray balls), a rigid linker (cyan) and a jumonji domain (green) followed by a four-helix bundle. (d) The KIAA1718 PHD domain contains a surface hydrophobic cage, a presumptive site for binding of H3K4me3. In the crystal lattice, the cage is blocked by the N-terminal prolines of a crystallographic symmetry-related molecule (Supplementary Fig. 6c).