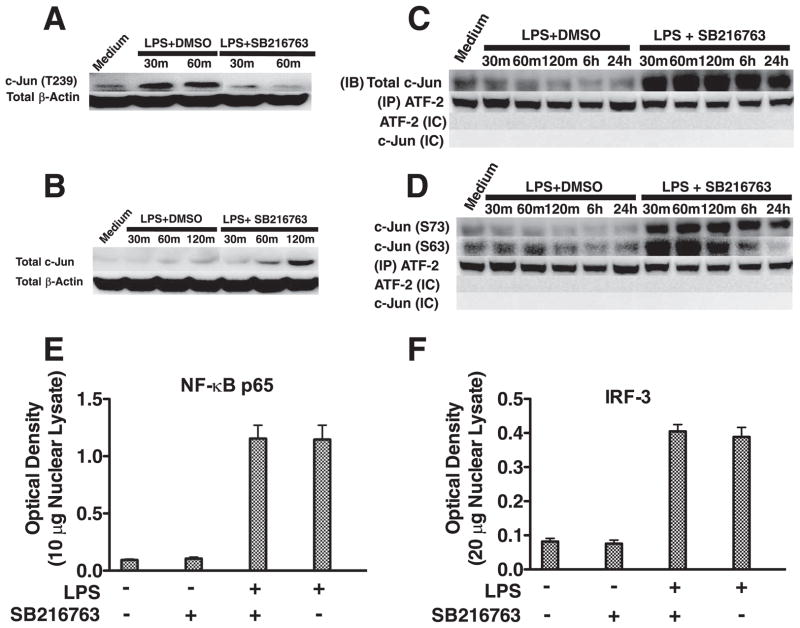
FIGURE 3.
GSK3 negatively affects the levels of nuclear c-Jun/ATF-2 heterodimer complexes by controlling total c-Jun levels. Inhibition of GSK3 attenuates the levels of phospho-c-Jun (Thr239) (A) and increases total c-Jun levels (B) in LPS-stimulated macrophages. GSK3 inhibition increases the association of total (C) and phospho-c-Jun (Ser63/73) (D) to ATF-2 in LPS-stimulated macrophages. In contrast to the effect of GSK3 inhibition of c-Jun, GSK3 inhibition did not discernibly affect the nuclear levels of the transcription factors NF-κB (E) or IRF-3 (F). A and B, Cell lysates were prepared at the given time points, and 15 μg of total protein was analyzed by immunoblot using Abs to c-Jun (Thr239) or total c-Jun, stripped, and reprobed with an Ab to total β-actin to ensure equal protein loading. C and D, Nuclear lysates were prepared at the given time points, a rabbit isotype control (IC) IgG or total ATF-2 was immunoprecipitated, and associated total (C) and phospho-c-Jun (Ser63/73) (D) were determined by immunoblot. C and D, Total ATF-2 was monitored by immunoblot between groups to ensure equivalent pull-down of ATF-2. C and D, No immunoreactive bands were detected at 43 or 48 kDa (c-Jun) or 65–75 kDa (ATF-2) when a rabbit isotype control (IC) Ab was used for immunoprecipitation. E and F, The transcription factor binding levels of NF-κB p65 (E) using 10 μg of nuclear lysate or IRF-3 (F) using 20 μg of nuclear lysate were obtained from macrophages stimulated with LPS for 6h. A–D, Data are representative of three separate experiments. E and F, Data represent the mean ± SD of three separate experiments.