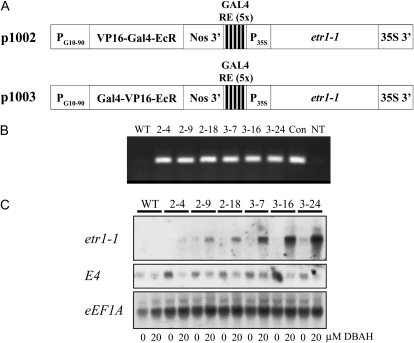
Figure 1.
Induction of etr1-1 expression from p1002 and p1003 in tomato. A, p1002 and p1003 constructs illustrating the expression of the VP16-GAL4-EcR (p1002) and GAL4-VP16-EcR (p1003) fusions from the PG10-90 promoter and the expression of etr1-1 from the DBAH-inducible, modified 35S promoter. B, PCR amplification of the etr1-1 transgene from three lines containing p1002 (i.e. 2-4, 2-9, 2-18) and three lines containing p1003 (i.e. 3-7, 3-16, 3-24), confirming the presence of the transgene in the transformants. PCR analysis of wild-type seeds (WT) and a reaction containing no template (NT) were included as negative controls. PCR amplification of the etr1-1 transgene from p1003 was included as a positive control (Con). C, Northern analysis of seedlings of the same p1002 and p1003 lines germinated in the dark for 14 d on medium with 20 μm ACC and with or without 20 μm DBAH. The level of etr1-1 expression in the absence or presence of the inducer was measured, as was the expression of the ethylene-inducible E4 mRNA using the same membrane after it had been stripped. Expression of eEF1A mRNA was determined from the same membrane as an RNA-loading control.