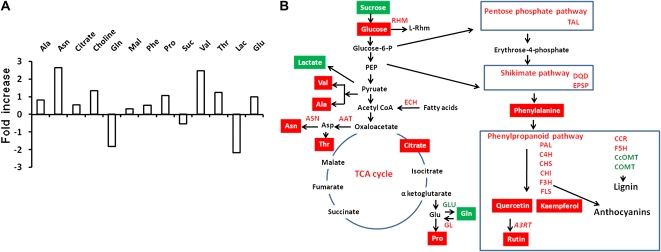
Figure 3.
Effects of AtMYB12 expression on different metabolites and metabolic sectors of tobacco leaves. A, Modulation of different metabolites as identified using a 400-MHz 1H NMR spectrum of aqueous methanolic extracts of leaves of wild-type and transgenic tobacco plants in D2O buffer. Data were recorded for at least three independent leaves (Table I) and plotted as fold change in each transgenic line with respect to the wild type. B, Schematic representation based on limited metabolite profiling and transcriptome analysis of the metabolic sectors altered in tobacco plants expressing AtMYB12. Red and green boxes show metabolites with increased and decreased contents, respectively, in AtMYB12-expressing lines in comparison with the wild type; enzymes encoded by different genes are shown in italics either in red or green representing up- or down-regulation in AtMYB12-expressing lines. Different metabolites are as follows: Lac, lactose; Mal, malate; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; Rhm, UDP-l-Rha. Enzymes encoded by differentially regulated genes are as follows: A3RT, anthocyanin 3-O-glucoside rhamnosyltransferase; AAT, Asp aminotransferase; ASN, Asn synthase; C4H, cinnamate 4-hydroxylase; CcOMT, caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase; CCR, cinnamoyl-CoA reductase; CHI, chalcone isomerase; CHS, chalcone synthase; COMT, catechol O-methyltransferase; DQD, 3-dehydroquinate dehydratase/shikimate dehydrogenase; ECS, enoyl-CoA hydratase/isomerase; EPSP, 5-enoylpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase; F3H, flavonone-3-hydroxylase; F5H, ferulate-5-hydroxylase; FLS, flavonol synthase; GL, Glu synthase; GLU, Gln synthetase; PAL, Phe ammonia lyase; RHM, Rha synthase; TAL, transaldolase. [See online article for color version of this figure.]