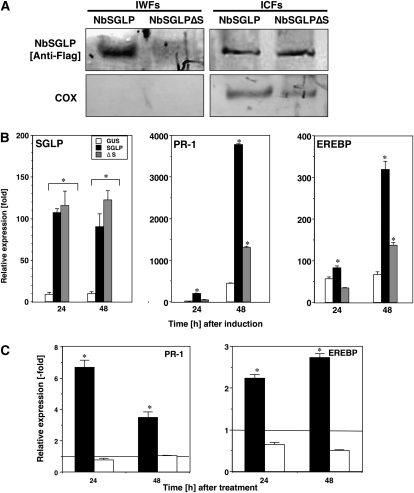
Figure 9.
Transient expression of NbSGLP and induction of defense-related genes in N. benthamiana. A, The IWFs and ICFs were prepared from N. benthamiana leaves inoculated with full-length NbSGLP- and signal peptide-deleted NbSGLPΔS- expressing A. tumefaciens. Both IWFs and ICFs were separated by 15% SDS-PAGE and then electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. The blots were subjected to western-blot analyses with monoclonal antibodies raised against the Flag tag sequence (NbSGLP [Anti-Flag]) and cytochrome oxidase (COX). B, Total RNA was isolated from N. benthamiana leaves inoculated with GUS, full-length NbSGLP-, and signal peptide-deleted NbSGLPΔS-expressing A. tumefaciens at the indicated time points. C, Total RNA was isolated from N. benthamiana leaves treated with the IWF fraction from NbSGLP-expressing (black bars) or NbSGLPΔS-expressing (white bars) leaves. The relative abundances of PR-1a and EREBP transcripts were analyzed using quantitative real-time PCR with primer combinations described in Supplemental Table S1. Expression values of NbSGLP, PR-1a, and EREBP are relative to the absolute nontreated control level and are normalized against the actin values. Lines showed expression levels of respective genes in nontreated control plants. Values represent means and sd from triplicate experiments. Asterisks denote values significantly different from nontreated controls (P < 0.05).