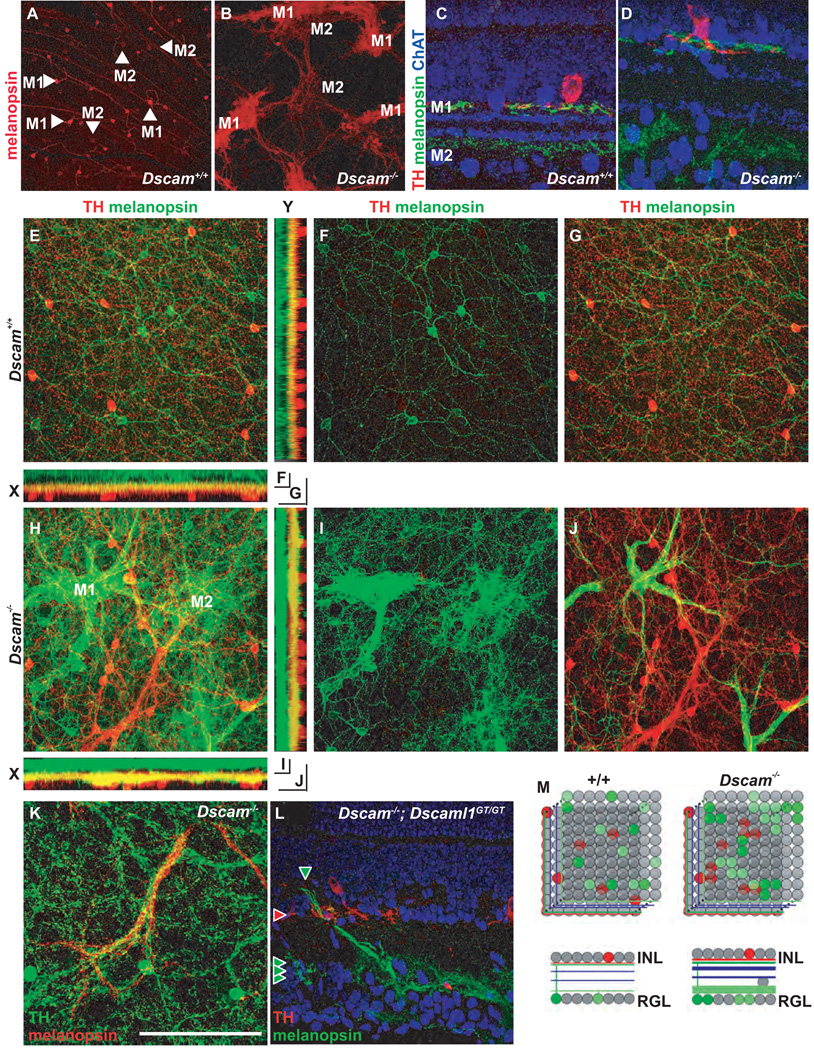
Figure 5. Confocal projection of ipRGCs and DA cells.
Wild type and Dscam−/− retinas were stained with antibodies to TH and melanopsin to detect DA cells and ipRGCs, respectively. A, Anti-melanopsin stains two populations of ipRGC, bright M1 cells and dim M2 cells in the wild type retina. B, In the Dscam−/− retina M1 and M2 cells aggregate and fasciculate separately. C and D, Cross-sections of wild type and Dscam−/− retina stained with antibodies to melanopsin, TH and ChAT. C, In the wild type retina ChAT labels the neurites of cholinergic amacrine cells in the ON and OFF portion of the INL, while M1 ipRGC dendrites costratify with DA neurites immediately below the INL and M2 dendrites stratify in the ON portion of the INL proximal to the RGL. D, This lamination pattern is preserved in the Dscam−/− retina. E, A confocal Z-projection from the RGL through the IPL to the amacrine cell bodies in the INL in the wild type retina. F, The bottom half of the Z-stack contains ganglion cell bodies and the M2 dendrites in the ON portion of the IPL. G, The top half contains dopaminergic amacrine cell bodies and M1 dendrites. H–J, In the Dscam−/− retina, melanopsin-positive dendrites stratify in two bands, with the IPL proximal band costratifying with DA neurites. I, Dim M2 cells stratify dendrites in the ON portion of the IPL. J, Bright M1 cell dendrites project to the IPL immediately below the INL. K, Cofasciculation of DA cell neurites and M1 dendrites is observed in the Dscam−/− retinas. L, In Dscam−/−; Dscaml1−/− double mutant retinas, ipRGC dendrites are fasciculated in the ON portion of the IPL, while dopaminergic amacrine neurites are fasciculated in the OFF portion of the IPL proximal to the INL; however, colamination in S1 is very disorganized. M, Dscam is required for mosaic patterning of DA and ipRGCs but gross synaptic lamination is intact. The measurement bar in panel (K) is equivalent to 496.8 µm in A and B, 64.1 µm in C and D, 193.75 µm in E-J and 132 µm in K.