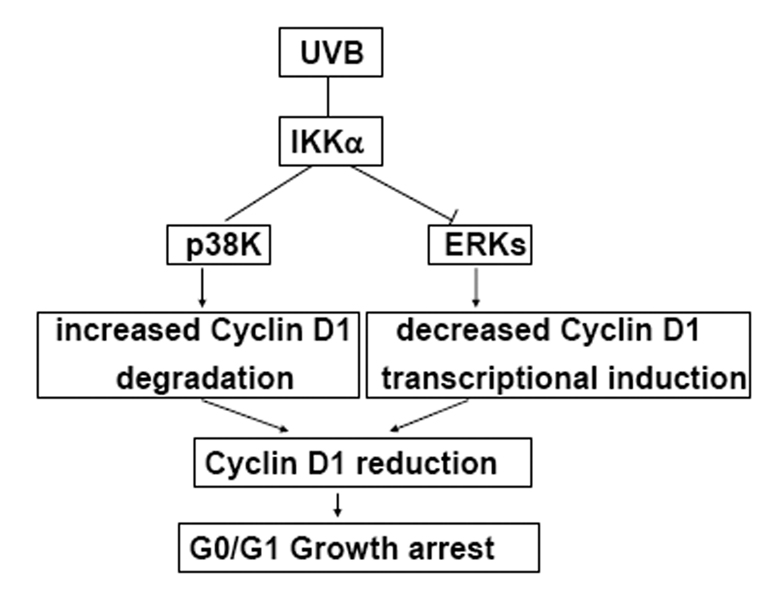
Figure 6. Proposed scheme of the role of IKKα in mediating the UVB-induced G0/G1 cell cycle arrest response by suppressing Cyclin D1 expression.
Under UVB exposure, we demonstrate a dual role of IKKα to selectively activate p38K and suppress ERKs activation in the early and late phases, respectively. The activation of p38K subsequently results in increased phosphorylation and degradation of Cyclin D1; while the inhibition on ERKs activation suppresses the induced transcription of cyclin d1 under UVB irradiation. Due to decreased protein stability and transcriptional suppression, the Cyclin D1 level is downregulated in response to UVB and therefore cell cycle progression is arrested at G0/G1 phase.