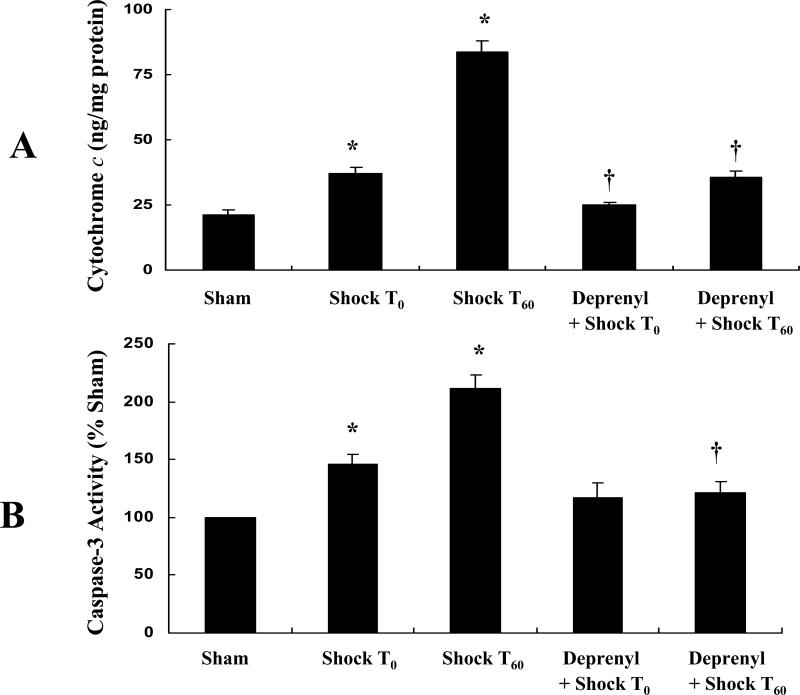
Figure 4.
A. (-)-Deprenyl prevents hemorrhagic shock induced release of cytochrome c from mitochondria to the cytosol in rat mesenteric vasculature. Hemorrhagic shock for 1 hour followed by 0 or 60 minutes of resuscitation (T0 or T60) significantly increases the cytosolic cytochrome c levels. *(p < 0.05; n = 5). (-)-Deprenyl treatment 10 minutes prior to hemorrhagic shock (T0 or T60) decreases cytochrome c levels compared with hemorrhagic shock groups without (-)-deprenyl treatment. †(p < 0.05; n = 5). B. (-)-Deprenyl prevents hemorrhagic shock induced activitation of caspase-3 in rat mesenteric vasculature. Hemorrhagic shock for 1 hour followed by 0 or 60 minutes of resuscitation (T0 or T60) significantly increased the caspase-3 activity. *(p < 0.05; n = 5). (-)-Deprenyl treatment 10 minutes prior to hemorrhagic shock (T60) significantly attenuates caspase-3 activity compared with hemorrhagic shock (T60) group without (-)-deprenyl treatment. †(p < 0.05; n = 5).